This is a preprint.
Interpretation of coefficients in segmented regression for interrupted time series analyses
- PMID: 38464266
- PMCID: PMC10925407
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3972428/v1
Interpretation of coefficients in segmented regression for interrupted time series analyses
Update in
-
Interpretation of coefficients in segmented regression for interrupted time series analyses.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2025 Apr 16;25(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12874-025-02556-8. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2025. PMID: 40241025 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Segmented regression, a common model for interrupted time series (ITS) analysis, primarily utilizes two equation parametrizations. Interpretations of coefficients vary between the two segmented regression parametrizations, leading to occasional user misinterpretations.
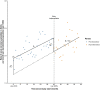
Methods: To illustrate differences in coefficient interpretation between two common parametrizations of segmented regression in ITS analysis, we derived analytical results and present an illustration evaluating the impact of a smoking regulation policy in Italy using a publicly accessible dataset. Estimated coefficients and their standard errors were obtained using two commonly used parametrizations for segmented regression with continuous outcomes. We clarified coefficient interpretations and intervention effect calculations.
Results: Our investigation revealed that both parametrizations represent the same model. However, due to differences in parametrization, the immediate effect of the intervention is estimated differently under the two approaches. The key difference lies in the interpretation of the coefficient related to the binary indicator for intervention implementation, impacting the calculation of the immediate effect.
Conclusions: Two common parametrizations of segmented regression represent the same model but have different interpretations of a key coefficient. Researchers employing either parametrization should exercise caution when interpreting coefficients and calculating intervention effects.
Keywords: coefficient interpretation; healthcare policy evaluation; interrupted time series design; observational study; segmented regression.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ramsay CR, Matowe L, Grilli R, Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE. Interrupted time series designs in health technology assessment: lessons from two systematic reviews of behavior change strategies. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2003;19(4):613–23. - PubMed
-
- Wagner AK, Soumerai SB, Zhang F, Ross-Degnan D. Segmented regression analysis of interrupted time series studies in medication use research. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2002;27(4):299–309. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

