Meta-analysis of factors influencing anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 38464355
- PMCID: PMC10921178
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i2.180
Meta-analysis of factors influencing anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a mature procedure recommended for correcting knee osteoarthritis deformity, relieving pain, and restoring normal biomechanics. Although TKA is a successful and cost-effective procedure, patient dissatisfaction is as high as 50%. Knee pain after TKA is a significant cause of patient dissatisfaction; the most common location for residual pain is the anterior region. Between 4% and 40% of patients have anterior knee pain (AKP).
Aim: To investigate the effect of various TKA procedures on postoperative AKP.
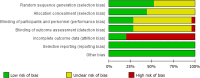
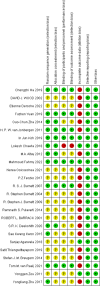
Methods: We searched PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane from January 2000 to September 2022. Randomized controlled trials with one intervention in the experimental group and no corresponding intervention (or other interventions) in the control group were collected. Two researchers independently read the title and abstract of the studies, preliminarily screened the articles, and read the full text in detail according to the selection criteria. Conflicts were resolved by consultation with a third researcher. And relevant data from the included studies were extracted and analyzed using Review Manager 5.4 software.
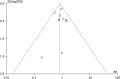
Results: There were 25 randomized controlled trials; 13 were comparative studies with or without patellar resurfacing. The meta-analysis showed no significant difference between the experimental and control groups (P = 0.61). Six studies were comparative studies of circumpatellar denervation vs non-denervation, divided into three subgroups for meta-analysis. The two-subgroup meta-analysis showed no significant difference between the experimental and the control groups (P = 0.31, P = 0.50). One subgroup meta-analysis showed a significant difference between the experimental and control groups (P = 0.001). Two studies compared fixed-bearing TKA and mobile-bearing TKA; the results meta-analysis showed no significant difference between the experimental and control groups (P = 0.630). Two studies compared lateral retinacular release vs non-release; the meta-analysis showed a significant difference between the experimental and control groups (P = 0.002); two other studies compared other factors.
Conclusion: Patellar resurfacing, mobile-bearing TKA, and fixed-bearing TKA do not reduce the incidence of AKP. Lateral retinacular release can reduce AKP; however, whether circumpatellar denervation can reduce AKP is controversial.
Keywords: Anterior knee pain; Interventions; Knee osteoarthritis; Meta-analysis; Total knee arthroplasty.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Hussain SM, Neilly DW, Baliga S, Patil S, Meek R. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of management options. Scott Med J. 2016;61:7–16. - PubMed
-
- Gill GS, Joshi AB. Long-term results of cemented, posterior cruciate ligament-retaining total knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis. Am J Knee Surg. 2001;14:209–214. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

