Serum tumor markers expression (CA199, CA242, and CEA) and its clinical implications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 38464372
- PMCID: PMC10921164
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.232
Serum tumor markers expression (CA199, CA242, and CEA) and its clinical implications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Glucose and lipid metabolic disorder in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with the levels of serum tumor markers of the digestive tract, such as cancer antigen (CA)199. Therefore, tumor markers in T2DM are important.
Aim: To evaluate the expression of serum tumor markers [CA199, CA242, and car-cinoembryonic antigen (CEA)] and the clinical implications of the expression in T2DM.
Methods: For this observational study conducted at Hefei BOE Hospital, China, we enrolled 82 patients with first-onset T2DM and 51 controls between April 2019 and December 2020. Levels of fasting blood glucose (FBG), tumor markers (CA199, CEA, and CA242), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), etc. were measured and group index levels were compared. Moreover, FBG and HbA1c levels were correlated with tumor marker levels. Tumor markers were tested for diagnostic accuracy in patients with > 9% HbA1c using the receiver operating curve (ROC) curve.
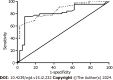
Results: The T2DM group had high serum FBG, HbA1c, CA199, and CEA levels (P < 0.05). A comparative analysis of the two groups based on HbA1c levels (Group A: HbA1c ≤ 9%; Group B: HbA1c > 9%) revealed significant differences in CEA and CA199 levels (P < 0.05). The areas under the ROC curve for CEA and CA199 were 0.853 and 0.809, respectively. CA199, CEA, and CA242 levels positively correlated with HbA1c (r = 0.308, 0.426, and 0.551, respectively) and FBG levels (r = 0.236, 0.231, and 0.298, respectively).
Conclusion: As compared to controls, serum CEA and CA199 levels were higher in patients with T2DM. HbA1c and FBG levels correlated with CA199, CEA, and CA242 levels. Patients with poorly controlled blood sugar must be screened for tumor markers.
Keywords: Cancer antigen 199; Cancer antigen 242; Carcinoembryonic antigen; Glycosylated hemoglobin; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Pearson-Stuttard J, Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Cividini S, Kakourou A, Gill D, Rizos EC, Monori G, Ward HA, Kyrgiou M, Gunter MJ, Tsilidis KK. Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer: An Umbrella Review of Observational and Mendelian Randomization Studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021;30:1218–1228. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scherübl H. [Type-2-diabetes and cancer risk] Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2021;146:1218–1225. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous