Dermatomyositis: Practical Guidance and Unmet Needs
- PMID: 38464459
- PMCID: PMC10924937
- DOI: 10.2147/ITT.S381472
Dermatomyositis: Practical Guidance and Unmet Needs
Abstract
Dermatomyositis is a heterogeneous idiopathic inflammatory myopathy associated with various cutaneous manifestations and variable presence of myositis, interstitial lung disease, and other visceral organ involvement. An accurate diagnosis of dermatomyositis requires correlating clinical examination findings with serological and histological findings. Familiarity with pathognomonic and common cutaneous manifestations of dermatomyositis, which are highlighted here, can be especially helpful in making an accurate diagnosis. Additionally, evaluating patients for presence of myositis-specific autoantibodies can further support or refute a dermatomyositis diagnosis. When present, myositis-specific autoantibodies can also help guide workups for various dermatomyositis-associated manifestations, as each is associated with relatively distinct clinical characteristics. Evaluating patients for various systemic manifestations often relies on expert opinion recommendations; however, societal guideline statements concerning the evaluation of some manifestations have recently been described. Although malignancy-associated dermatomyositis is a well-accepted subtype, there is limited evidence to support extensive malignancy screening has a favorable benefit-risk ratio in most dermatomyositis patients. However, recent research has uncovered novel associations between dermatomyositis and malignancy, suggesting the possibility of identifying high-risk subsets of dermatomyositis patients in whom malignancy screening may have a high value. Treatment for dermatomyositis has remained largely unchanged over the past several decades. Although many dermatomyositis patients can be effectively treated with current options, either as monotherapy or with combination regimens, there is a need for more targeted and effective DM therapies, in general, and for MDA5(+) dermatomyositis-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Fortunately, significant current and emerging research activities evaluating various novel medications for dermatomyositis provide hope for exciting future advances in patients with this intriguing immune-mediated disease.
Keywords: MDA-5; autoantibody; idiopathic inflammatory myopathy; malignancy; myositis; treatment.
© 2024 Cassard et al.
Conflict of interest statement
APF: Investigator for Pfizer, Corbus, Mallinckrodt, Alexion, Priovant, and Novartis receives personal research support from Mallinckrodt and Novartis; honorarium from AbbVie, BMS, Biogen, Novartis, and UCB for consultation and advisory board participation; and honorarium from AbbVie, Novartis, BMS, Kyowa Kirin, and Mallinckrodt for teaching and speaking. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this work.
Figures
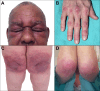
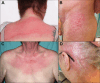
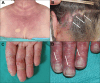
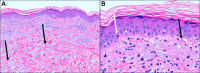
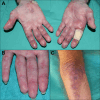
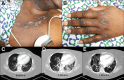
References
-
- Rothwell S, Cooper RG, Lundberg IE, et al. Dense genotyping of immune-related loci in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies confirms HLA alleles as the strongest genetic risk factor and suggests different genetic background for major clinical subgroups. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(8):1558–1566. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208119 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

