AI energized hydrogel design, optimization and application in biomedicine
- PMID: 38464497
- PMCID: PMC10924066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101014
AI energized hydrogel design, optimization and application in biomedicine
Abstract
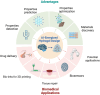
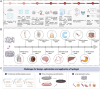
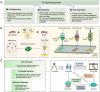
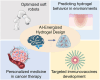
Traditional hydrogel design and optimization methods usually rely on repeated experiments, which is time-consuming and expensive, resulting in a slow-moving of advanced hydrogel development. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) technology and increasing material data, AI-energized design and optimization of hydrogels for biomedical applications has emerged as a revolutionary breakthrough in materials science. This review begins by outlining the history of AI and the potential advantages of using AI in the design and optimization of hydrogels, such as prediction and optimization of properties, multi-attribute optimization, high-throughput screening, automated material discovery, optimizing experimental design, and etc. Then, we focus on the various applications of hydrogels supported by AI technology in biomedicine, including drug delivery, bio-inks for advanced manufacturing, tissue repair, and biosensors, so as to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of researchers in this field. Finally, we discuss the future directions and prospects, and provide a new perspective for the research and development of novel hydrogel materials for biomedical applications.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Biomedicine application; Design; Hydrogel; Optimization.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Exploring the Potential of Artificial Intelligence for Hydrogel Development-A Short Review.Gels. 2023 Oct 25;9(11):845. doi: 10.3390/gels9110845. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37998936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Drug Formulation and Development: Applications and Future Prospects.Curr Drug Metab. 2023;24(9):622-634. doi: 10.2174/0113892002265786230921062205. Curr Drug Metab. 2023. PMID: 37779408 Review.
-
Research prospects and AI-driven strategies for metal-organic framework-hydrogel composite materials in cancer treatment.RSC Med Chem. 2025 May 1. doi: 10.1039/d5md00207a. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40395219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Fundamental Optimization Approaches and the Role of AI Enabling Technologies in Physical Layer Security.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 9;22(9):3589. doi: 10.3390/s22093589. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35591279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical Technology and Drug Delivery Design.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 10;15(7):1916. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071916. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating machine learning for the optimization of polyacrylamide/alginate hydrogel.Regen Biomater. 2024 Sep 2;11:rbae109. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae109. eCollection 2024. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39323746 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence powers regenerative medicine into predictive realm.Regen Med. 2024 Dec;19(12):611-616. doi: 10.1080/17460751.2024.2437281. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Regen Med. 2024. PMID: 39660914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scalable Accelerated Materials Discovery of Sustainable Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels by Autonomous Experimentation and Collaborative Learning.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Dec 25;16(51):70310-70321. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c16614. Epub 2024 Dec 11. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39661966 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin-induced small extracellular vesicles under GelMA scaffolds facilitate diabetic wound repair through accelerating angiogenesis and alleviating macrophage-mediated inflammation via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Mater Today Bio. 2025 May 6;32:101846. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101846. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40469695 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advancements in Smart Hydrogel-Based Materials in Cartilage Tissue Engineering.Materials (Basel). 2025 May 31;18(11):2576. doi: 10.3390/ma18112576. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ehsan Nazarzadeh Z., Danial K., Atefeh Z., Hulya Y., Tarun A., Sara H., Reza M., Fatma O., Onur S., Sevin A., Haroon K., Ali Z., Esmaeel S., Arun K., Ebrahim M., Negar Hosseinzadeh K., Virgilio M., Feng Z., Vadim J., Alireza Hassani N., Ali K. Biomedical applications of engineered heparin-based materials. Bioact. Mater. 2023;31:87. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li M., Yu B., Wang S., Zhou F., Cui J., Su J. Microenvironment-responsive nanocarriers for targeted bone disease therapy. Nano Today. 2023;50 doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2023.101838. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

