Immune checkpoint inhibitors and acute kidney injury
- PMID: 38464524
- PMCID: PMC10920224
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1353339
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and acute kidney injury
Abstract
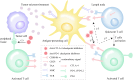
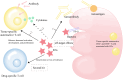
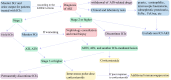
As a new type of anti-tumor immunotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have improved the prognosis of multiple malignancies. However, renal complications are becoming more frequent. Nephrotoxicity often manifests as acute kidney injury (AKI), and the most common histopathological type is acute tubulointerstitial nephritis (ATIN). Based on previous studies of the incidence and potential risk factors for nephrotoxicity, in this review, we describe the mechanism of AKI after ICIs treatment, summarize the incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of AKI, and discuss the diagnosis and management of immune checkpoint inhibitors-associated acute kidney injury (ICI-AKI). In addition, we review the current status of ICIs rechallenge and the therapeutic strategies of ICIs applied in kidney transplant recipients. Finally, we emphasize the importance of collaboration between nephrologists and oncologists to guide the treatment of ICIs and the management of renal complications.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune-related adverse events; immunotherapy; malignancies; nephrotoxicity.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Gao, Kong, Wang, Si, Han, Li, Lv and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. . Five-year survival and correlates among patients with advanced melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, or non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. JAMA Oncol. (2019) 5:1411–20. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2187. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

