Antigenic epitope targets of rhesus macaques self-curing from Schistosoma mansoni infection
- PMID: 38464672
- PMCID: PMC10921417
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1269336
Antigenic epitope targets of rhesus macaques self-curing from Schistosoma mansoni infection
Abstract
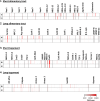
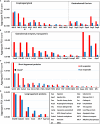
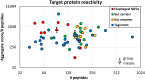
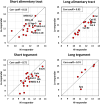
The self-cure of rhesus macaques from a schistosome infection and their subsequent strong immunity to a cercarial challenge should provide novel insights into the way these parasites can be eliminated by immunological attack. High-density arrays comprising overlapping 15-mer peptides from target proteins printed on glass slides can be used to screen sera from host species to determine antibody reactivity at the single epitope level. Careful selection of proteins, based on compositional studies, is crucial to encompass only those exposed on or secreted from the intra-mammalian stages and is intended to focus the analysis solely on targets mediating protection. We report the results of this approach using two pools of sera from hi- and lo-responder macaques undergoing self-cure, to screen arrays comprising tegument, esophageal gland, and gastrodermis proteins. We show that, overall, the target epitopes are the same in both groups, but the intensity of response is twice as strong in the high responders. In addition, apart from Sm25, tegument proteins elicit much weaker responses than those originating in the alimentary tract, as was apparent in IFNγR KO mice. We also highlight the most reactive epitopes in key proteins. Armed with this knowledge, we intend to use multi-epitope constructs in vaccination experiments, which seek to emulate the self-cure process in experimental animals and potentially in humans.
Keywords: alimentary tract proteins; antigenic targets; epitope mapping; esophageal glands; peptide array; tegument proteins.
Copyright © 2024 Vance, Khouri, Neto, James, Leite, Farias and Wilson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that a patent related to this work has been deposited at INPI ((Instituto Nacional de Propriedade Intelectual): BR 10 2024 002799. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Models of Protective Immunity against Schistosomes: Implications for Vaccine Development.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 3;12(10):1215. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101215. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37887731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epitope Mapping of Exposed Tegument and Alimentary Tract Proteins Identifies Putative Antigenic Targets of the Attenuated Schistosome Vaccine.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 3;11:624613. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.624613. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33763055 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the epitopes of Schistosoma japonicum esophageal gland proteins for incorporation into vaccine constructs.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 27;15(2):e0229542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229542. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32107503 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma mansoni gene GP22 encodes the tegumental antigen sm25: (1) antibodies to a predicted B-cell epitope of Sm25 cross-react with other candidate vaccine worm antigens; (2) characterization of a recombinant product containing tandem-repeats of this peptide as a vaccine.Parasite Immunol. 2000 Aug;22(8):381-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.2000.00316.x. Parasite Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10972845
-
Evidence That Rhesus Macaques Self-Cure from a Schistosoma japonicum Infection by Disrupting Worm Esophageal Function: A New Route to an Effective Vaccine?PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Jul 10;9(7):e0003925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003925. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26161644 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Models of Protective Immunity against Schistosomes: Implications for Vaccine Development.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 3;12(10):1215. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101215. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37887731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lindholz CG, Favero V, Verissimo CM, Candido RRF, de Souza RP, Dos Santos RR, et al. . Study of diagnostic accuracy of Helmintex, Kato-Katz, and POC-CCA methods for diagnosing intestinal schistosomiasis in Candeal, a low intensity transmission area in northeastern Brazil. PloS Negl Trop Dis (2018) 12(3):e0006274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006274 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui AJ, Molehin AJ, Zhang W, Ganapathy PK, Kim E, Rojo JU, et al. . Sm-p80-based vaccine trial in baboons: efficacy when mimicking natural conditions of chronic disease, praziquantel therapy, immunization, and Schistosoma mansoni re-encounter. Ann N Y Acad Sci (2018) 1425(1):19–37. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13866 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

