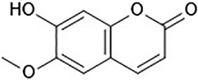
Scopoletin: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity
- PMID: 38464713
- PMCID: PMC10923241
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1268464
Scopoletin: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity
Abstract
Scopoletin is a coumarin synthesized by diverse medicinal and edible plants, which plays a vital role as a therapeutic and chemopreventive agent in the treatment of a variety of diseases. In this review, an overview of the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity of scopoletin is provided. In addition, the prospects and outlook for future studies are appraised. Scopoletin is indicated to have antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-inflammation, anti-angiogenesis, anti-oxidation, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, hepatoprotective, and neuroprotective properties and immunomodulatory effects in both in vitro and in vivo experimental trials. In addition, it is an inhibitor of various enzymes, including choline acetyltransferase, acetylcholinesterase, and monoamine oxidase. Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated the low bioavailability, rapid absorption, and extensive metabolism of scopoletin. These properties may be associated with its poor solubility in aqueous media. In addition, toxicity research indicates the non-toxicity of scopoletin to most cell types tested to date, suggesting that scopoletin will neither induce treatment-associated mortality nor abnormal performance with the test dose. Considering its favorable pharmacological activities, scopoletin has the potential to act as a drug candidate in the treatment of cancer, liver disease, diabetes, neurodegenerative disease, and mental disorders. In view of its merits and limitations, scopoletin is a suitable lead compound for the development of new, efficient, and low-toxicity derivatives. Additional studies are needed to explore its molecular mechanisms and targets, verify its toxicity, and promote its oral bioavailability.
Keywords: pharmacokinetics; pharmacological activities; plant sources; scopoletin; toxicology.
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Li, Zhang and Bai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Acharya D., Bogati B., Risal P. (2013). Scopoletin reduces intracellular survival of Salmonella typhi within U937 human macrophage cell line in vitro . Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 1 (6), 47–51.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources