Associations between one-carbon metabolism and valproic acid-induced liver dysfunction in epileptic patients
- PMID: 38464726
- PMCID: PMC10924308
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1358262
Associations between one-carbon metabolism and valproic acid-induced liver dysfunction in epileptic patients
Abstract
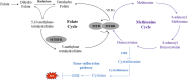
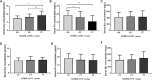
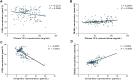
Valproic acid (VPA) has been widely used as an antiepileptic drug for decades. Although VPA is effective and well-tolerated, long-term VPA treatment is usually associated with hepatotoxicity. However, the underlying mechanisms of VPA-caused hepatotoxicity remain unclear. In this study, a total of 157 pediatric patients with epilepsy were recruited and divided into normal liver function (NLF, 112 subjects) group and abnormal liver function (ABLF, 45 subjects) group. We observed that MTHFR A1298C and MTHFR C677T variants may be linked to VPA-induced liver dysfunction (p = 0.001; p = 0.023, respectively). We also found that the MTHFR A1298C polymorphism was associated with a higher serum Hcy level (p = 0.001) and a lower FA level (p = 0.001). Moreover, the serum Hcy levels was strongly correlated with the GSH and TBARS concentrations (r = -0.6065, P < 0.001; r = 0.6564, P < 0.001, respectively). Furthermore, logistic analysis indicated that MTHFR A1298C/C677T polymorphisms and increased Hcy concentrations may be risk factors for VPA-induced liver dysfunction. These results suggested that individual susceptibility to VPA-induced liver dysfunction may result from MTHFR A1298C/C677T polymorphisms and increased Hcy levels. This study may be helpful for the prevention and guidance of VPA-induced liver dysfunction.
Keywords: MTHFR A1298C; MTHFR C677T; Valproic acid; homocysteine; liver dysfunction; one-carbon metabolism; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Wang, Sun, Wang, Xu, Yang, Du, Zhou, Qi and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the relationship between C677T variants of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene and hyperhomocysteinemia in children receiving antiepileptic drug therapy.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Apr 1;32(3):844-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.12.018. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18234410
-
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T and A1298C polymorphisms: genotype frequency and association with homocysteine and folate levels in middle-southern Italian adults.Cell Biochem Funct. 2014 Jan;32(1):1-4. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3019. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014. PMID: 24277487
-
Association of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphisms with serum folate, cobalanin and homocysteine concentrations in Greek adults.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023 Apr;83(2):69-73. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2023.2167232. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023. PMID: 36662122
-
Associations between C677T and A1298C polymorphisms of MTHFR and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rheumatol Int. 2017 Apr;37(4):557-569. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3650-4. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Rheumatol Int. 2017. PMID: 28175955
-
Associations between MTHFR gene polymorphisms (C677T and A1298C) and genetic susceptibility to prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2024 Jan 26;15:1343687. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1343687. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38343693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the patterns in traditional Chinese medicine for bipolar disorder: a data-driven network approach.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1524345. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1524345. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40535764 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbing Cholesterol/Sphingolipid Metabolism by Squalene Epoxidase Arises Crizotinib Hepatotoxicity.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(14):e2414923. doi: 10.1002/advs.202414923. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39836491 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

