Prediction of anticancer peptides derived from the true lectins of Phoenix dactylifera and their synergetic effect with mitotane
- PMID: 38464729
- PMCID: PMC10920327
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1322865
Prediction of anticancer peptides derived from the true lectins of Phoenix dactylifera and their synergetic effect with mitotane
Abstract
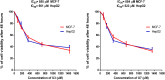
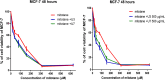
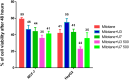
Background and aims: Cancer continues to be a significant source of both illness and death on a global scale, traditional medicinal plants continue to serve as a fundamental resource of natural bioactive compounds as an alternative source of remedies. Although there have been numerous studies on the therapeutic role of Phoenix dactylifera, the study of the role of peptides has not been thoroughly investigated. This study aimed to investigate the anticancer activity of lectin peptides from P. dactylifera using in silico and in vivo analysis. Methods: Different computational tools were used to extract and predict anticancer peptides from the true lectins of P. dactylifera. Nine peptides that are bioactive substances have been investigated for their anticancer activity against MCF-7 and T47D (two forms of breast cancer). To counteract the unfavorable effects of mitotane, the most potent peptides (U3 and U7) were combined with it and assessed for anticancer activity against MCF-7 and HepG2. Results: In silico analysis revealed that nine peptides were predicted with anticancer activity. In cell lines, the lowest IC50 values were measured in U3 and U7 against MCF-7 and T47D cells. U3 or U7 in combination with mitotane demonstrated the lowest IC50 against MCF-7 and HepG2. The maximum level of cell proliferation inhibition was 22% when U3 (500 µg/mL) and 25 µg/mL mitotane were combined, compared to 41% when 25 µg/mL mitotane was used alone. When mitotane and U3 or U7 were combined, it was shown that these bioactive substances worked synergistically with mitotane to lessen its negative effects. The combination of peptides and mitotane could be regarded as an efficient chemotherapeutic medication having these bioactive properties for treating a variety of tumors while enhancing the reduction of side effects.
Keywords: HepG2; MCF-7 breast cancer cells; date palm; in silico analysis; liver cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Baothman, Ali, Hosawi, Hassan E. Konozy, Abu Zeid, Ahmad and Altayb.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anticancer potential of Phoenix dactylifera L. seed extract in human cancer cells and pro-apoptotic effects mediated through caspase-3 dependent pathway in human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells: an in vitro and in silico investigation.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Mar 15;22(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03533-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35291987 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Heart Components Extracted from Iraqi Phoneix Dactylifera Chick.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Nov 1;22(11):3533-3541. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.11.3533. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34837910 Free PMC article.
-
Phoenix dactylifera (date palm; Arecaceae) putative lectin homologs: Genome-wide search, architecture analysis, and evolutionary relationship.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun;30(6):103676. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103676. Epub 2023 May 4. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37213699 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Composition and Biological Activities of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Seeds: A Review.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 3;12(11):1626. doi: 10.3390/biom12111626. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera): Novel Findings and Future Directions for Food and Drug Discovery.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019;16(1):2-10. doi: 10.2174/1570163815666180320111937. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019. PMID: 29557751 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of camel milk lactoferrin peptides against breast cancer cells: in silico and in vitro study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 19;15:1425504. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1425504. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39629082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdoullahi S., Jahangiri A., Halabian R. (2022). Potential role of herbal-and bacterial-derived peptides against colorectal cancer. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 32, 673–692. 10.1007/s43450-022-00276-4 - DOI
-
- Al Sawafi A. G., Al Maliki D. F. (2020). Assessment of rainwater pollution and bio-monitoring of trace metals air pollution by two types of plants in southern Iraq, Basrah city. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 23, 231–392. 10.36295/asro.2020.231392 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

