The endothelin receptor antagonist macitentan ameliorates endothelin-mediated vasoconstriction and promotes the survival of retinal ganglion cells in rats
- PMID: 38464735
- PMCID: PMC10921982
- DOI: 10.3389/fopht.2023.1185755
The endothelin receptor antagonist macitentan ameliorates endothelin-mediated vasoconstriction and promotes the survival of retinal ganglion cells in rats
Abstract
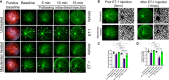
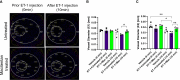
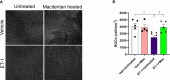
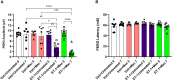
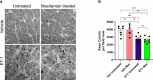
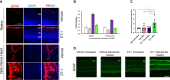
Glaucoma is a chronic and progressive eye disease, commonly associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) and characterized by optic nerve degeneration, cupping of the optic disc, and loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). The pathological changes in glaucoma are triggered by multiple mechanisms and both mechanical effects and vascular factors are thought to contribute to the etiology of glaucoma. Various studies have shown that endothelin-1 (ET-1), a vasoactive peptide, acting through its G protein coupled receptors, ETA and ETB, plays a pathophysiologic role in glaucoma. However, the mechanisms by which ET-1 contribute to neurodegeneration remain to be completely understood. Our laboratory and others demonstrated that macitentan (MAC), a pan endothelin receptor antagonist, has neuroprotective effects in rodent models of IOP elevation. The current study aimed to determine if oral administration of a dual endothelin antagonist, macitentan, could promote neuroprotection in an acute model of intravitreal administration of ET-1. We demonstrate that vasoconstriction following the intravitreal administration of ET-1 was attenuated by dietary administration of the ETA/ETB dual receptor antagonist, macitentan (5 mg/kg body weight) in retired breeder Brown Norway rats. ET-1 intravitreal injection produced a 40% loss of RGCs, which was significantly lower in macitentan-treated rats. We also evaluated the expression levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) at 24 h and 7 days post intravitreal administration of ET-1 in Brown Norway rats as well as following ET-1 treatment in cultured human optic nerve head astrocytes. We observed that at the 24 h time point the expression levels of GFAP was upregulated (indicative of glial activation) following intravitreal ET-1 administration in both retina and optic nerve head regions. However, following macitentan administration for 7 days after intravitreal ET-1 administration, we observed an upregulation of GFAP expression, compared to untreated rats injected intravitreally with ET-1 alone. Macitentan treatment in ET-1 administered rats showed protection of RGC somas but was not able to preserve axonal integrity and functionality. The endothelin receptor antagonist, macitentan, has neuroprotective effects in the retinas of Brown Norway rats acting through different mechanisms, including enhancement of RGC survival and reduction of ET-1 mediated vasoconstriction.
Keywords: endothelins; glaucoma; macitentan; neuroprotection; vasoconstriction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors RK and DS declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral administration of a dual ETA/ETB receptor antagonist promotes neuroprotection in a rodent model of glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2022 Aug 7;28:165-177. eCollection 2022. Mol Vis. 2022. PMID: 36274816 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the endothelin A (ETA) receptor and its association with neurodegeneration in a rodent model of glaucoma.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Mar 1;18(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0346-3. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28249604 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin B receptors contribute to retinal ganglion cell loss in a rat model of glaucoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043199. Epub 2012 Aug 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22916224 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin in the pulmonary circulation with special reference to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.Scand Cardiovasc J Suppl. 1997;46:1-40. Scand Cardiovasc J Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9265559 Review.
-
[A challenge to primary open-angle glaucoma including normal-pressure. Clinical problems and their scientific solution].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012 Mar;116(3):233-67; discussion 268. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22568103 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Combination of blockade of endothelin signalling and compensation of IGF1 expression protects the retina from degeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jan 22;81(1):51. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05087-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38252153 Free PMC article.
-
A Reduction in Mitophagy Is Associated with Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration in Rodent Models of Glaucoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 4;25(23):13040. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313040. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684751 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in patients with chronic glaucoma - a literature review.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024 Oct-Dec;65(4):557-565. doi: 10.47162/RJME.65.4.01. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024. PMID: 39957016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

