The potential of herbal drugs to treat heart failure: The roles of Sirt1/AMPK
- PMID: 38464786
- PMCID: PMC10921247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.09.001
The potential of herbal drugs to treat heart failure: The roles of Sirt1/AMPK
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is a highly morbid syndrome that seriously affects the physical and mental health of patients and generates an enormous socio-economic burden. In addition to cardiac myocyte oxidative stress and apoptosis, which are considered mechanisms for the development of HF, alterations in cardiac energy metabolism and pathological autophagy also contribute to cardiac abnormalities and ultimately HF. Silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1) and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent deacetylases and phosphorylated kinases, respectively. They play similar roles in regulating some pathological processes of the heart through regulating targets such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), protein 38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). We summarized the synergistic effects of Sirt1 and AMPK in the heart, and listed the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that exhibit cardioprotective properties by modulating the Sirt1/AMPK pathway, to provide a basis for the development of Sirt1/AMPK activators or inhibitors for the treatment of HF and other cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
Keywords: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; Heart failure; Silent information regulator 1; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
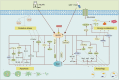
 indicates stimulation/promoting,
indicates stimulation/promoting,  indicates reduction/inhibition. ROS: reactive oxygen species; SOD: manganese-superoxide dismutase; GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FOXO4: forkhead box family and subfamily O of transcription factors 4; FOXO3: forkhead box family and subfamily O of transcription factors 3; NQO1: NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase 1; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; SAPK: stress-activated protein kinase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; BAD: Bcl-2 associated agonist of cell death; Bax: Bcl2-associated x; JNK: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa-B; p38 MAPK: protein 38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Nampt: nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase; eEF2K: elongation factor-2 kinase; eIF2α: eukaryotic initiation factor-2α; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin compound 1; mTORC2: mammalian target of rapamycin compound 2; Akt: protein kinase B; PINK: PTEN-induced kinase 1; ULK1: unc-51-like kinase 1; Atg5: autophagy-related genes 5; Atg7: autophagy-related genes 7; Atg8: autophagy-related genes 8; PFK-2: phosphofructokinase-2; AICAR: aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; AMP: adenosine monophosphate.
indicates reduction/inhibition. ROS: reactive oxygen species; SOD: manganese-superoxide dismutase; GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FOXO4: forkhead box family and subfamily O of transcription factors 4; FOXO3: forkhead box family and subfamily O of transcription factors 3; NQO1: NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase 1; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; SAPK: stress-activated protein kinase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; BAD: Bcl-2 associated agonist of cell death; Bax: Bcl2-associated x; JNK: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa-B; p38 MAPK: protein 38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Nampt: nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase; eEF2K: elongation factor-2 kinase; eIF2α: eukaryotic initiation factor-2α; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin compound 1; mTORC2: mammalian target of rapamycin compound 2; Akt: protein kinase B; PINK: PTEN-induced kinase 1; ULK1: unc-51-like kinase 1; Atg5: autophagy-related genes 5; Atg7: autophagy-related genes 7; Atg8: autophagy-related genes 8; PFK-2: phosphofructokinase-2; AICAR: aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; AMP: adenosine monophosphate.
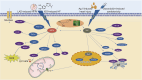
 indicates stimulation/promoting,
indicates stimulation/promoting,  indicates reduction/inhibition. LAD: ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery; MI/RI: myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury; ISO: isoprenaline; HF: heart failure; Ang II: angiotensin II; GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; AMPK: adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; LC-3: light chain 3; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2; NQO1: NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase 1; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; MPC Ⅰ/Ⅱ: mitochondrial pyruvate carrier Ⅰ/Ⅱ; p62: sequestosome 1; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; Akt: protein kinase B; Sirt1: silent information regulator 1; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor protein 3; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa-B; PPARα: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; JNK: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; PINK: PTEN-induced kinase 1; TMBIM6: transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif containing 6; CHOP: C/EBP-homologous protein; PERK: protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; TFAM: mitochondrial transcription factor A; FOXOs: forkhead box family and subfamily O of transcription factors; TCA: tricarboxylic acid; mPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: Bcl-2-associated x. The above herbal pictures are reprinted from Reprinted from
indicates reduction/inhibition. LAD: ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery; MI/RI: myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury; ISO: isoprenaline; HF: heart failure; Ang II: angiotensin II; GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; AMPK: adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; LC-3: light chain 3; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2; NQO1: NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase 1; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; MPC Ⅰ/Ⅱ: mitochondrial pyruvate carrier Ⅰ/Ⅱ; p62: sequestosome 1; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; Akt: protein kinase B; Sirt1: silent information regulator 1; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor protein 3; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa-B; PPARα: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; JNK: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; PINK: PTEN-induced kinase 1; TMBIM6: transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif containing 6; CHOP: C/EBP-homologous protein; PERK: protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; TFAM: mitochondrial transcription factor A; FOXOs: forkhead box family and subfamily O of transcription factors; TCA: tricarboxylic acid; mPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: Bcl-2-associated x. The above herbal pictures are reprinted from Reprinted from References
-
- Lippi G., Sanchis-Gomar F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med. J. 2020;5
-
- Shah Kevin S., Xu H.L., Matsouaka R.A., et al. Heart Failure with preserved, borderline, and reduced ejection fraction: 5-year outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017;70:2476–2486. - PubMed
-
- Del Buono M.G., Arena R., Borlaug B.A., et al. Exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019;73:2209–2225. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

