S-ICD Implantation in Secondary Prevention in a Young Patient With Recent Surgically Repaired Pectus Excavatum
- PMID: 38464794
- PMCID: PMC10920114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2024.102231
S-ICD Implantation in Secondary Prevention in a Young Patient With Recent Surgically Repaired Pectus Excavatum
Abstract
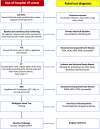
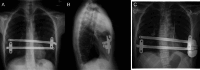
We report a case of successful implantation of a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in a young patient with severe pectus excavatum presenting with out-of-hospital ventricular fibrillation arrest who was recently surgically repaired with a MIRPE-Nuss procedure. No complications in lead positioning were observed, and the device was tested to determine that it functioned properly.
Keywords: Nuss procedure; S-ICD; electrophysiology; pectus excavatum; right ventricle; secondary prevention; sudden cardiac arrest; ventricular fibrillation.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Olivotto has received consulting fees from Cytokinetics and Bristol Myers Squibb. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in a patient with pectus excavatum.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013 May;36(5):e138-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2012.03413.x. Epub 2012 May 3. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013. PMID: 22554273
-
Successful intermuscular implantation of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in a Japanese patient with pectus excavatum.J Arrhythm. 2017 Feb;33(1):63-65. doi: 10.1016/j.joa.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Jun 1. J Arrhythm. 2017. PMID: 28217231 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest provoked by forward bending in adolescent with severe pectus excavatum.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021 Oct 25;5(10):ytab373. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytab373. eCollection 2021 Oct. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34738057 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden Cardiac Arrest in a Young Patient With Severe Pectus Excavatum.Am J Med Sci. 2018 Dec;356(6):570-573. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 9. Am J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30177261 Review.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy: patient outcomes, incidence of appropriate and inappropriate interventions, and complications.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013 Jun;6(3):562-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.113.000392. Epub 2013 May 14. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23673907 Review.
Cited by
-
Heart Disease and Pectus Excavatum: An Underestimated Issue-Single Center Experience and Literature Review.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 11;14(12):1643. doi: 10.3390/life14121643. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaroszewski D.E., Velazco C.S. Minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair (MIRPE) Oper Tech Thorac Cardiovas Surg. 2018;23:P198–P215.
-
- Droghetti A., Basso Ricci E., Scimia P., Harizai F., Marini M. Ultrasound-guided serratus anterior plane block combined with the two-incision technique for subcutaneous ICD implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;41(5):517–523. - PubMed
-
- Pimenta J., Vieira A., Henriques-Coelho T. Ventricular arrhythmia solved by surgical correction of pectus excavatum. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;26(4):706–708. - PubMed
-
- Desimone C.V., Sagar S., Moir C., Asirvatham S.J. Combined surgical and ablative cure for localized sternal compression-induced cardiomyopathy and ventricular tachyarrhythmia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;144(3):e85–e87. - PubMed
-
- Hamoud A., Barry J. Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in a patient with pectus excavatum. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013;36(5):e138–e139. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

