Coca-Cola consumption vs fragmentation in the management of patients with phytobezoars: A prospective randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38464817
- PMCID: PMC10921151
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i2.83
Coca-Cola consumption vs fragmentation in the management of patients with phytobezoars: A prospective randomized controlled trial
Abstract
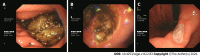
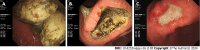
Background: Gastric phytobezoars (GPBs) are very common in northern China. Combined therapy involving carbonated beverage consumption and endoscopic lithotripsy has been shown to be effective and safe. Existing studies on this subject are often case reports highlighting the successful dissolution of phytobezoars through Coca-Cola consumption. Consequently, large-scale prospective investigations in this domain remain scarce. Therefore, we conducted a randomized controlled trial to examine the effects of Coca-Cola consumption on GPBs.
Aim: To evaluate the impact of Coca-Cola on GPBs, including the dissolution rate, medical expenses, ulcer rate, and operation time.
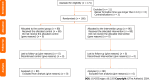
Methods: A total of 160 consecutive patients diagnosed with GPBs were allocated into two groups (a control group and an intervention group) through computer-generated randomization. Patients in the intervention group received a Coca-Cola-based regimen (Coca-Cola 2000-4000 mL per day for 7 d), while those in the control group underwent emergency fragmentation.
Results: Complete dissolution of GPBs was achieved in 100% of the patients in the intervention group. The disparity in expenses between the control group and intervention group (t = 25.791, P = 0.000) was statistically significant, and the difference in gastric ulcer occurrence between the control group and intervention group (χ2 = 6.181, P = 0.013) was also statistically significant.
Conclusion: Timely ingestion of Coca-Cola yields significant benefits, including a complete dissolution rate of 100%, a low incidence of gastric ulcers, no need for fragmentation and reduced expenses.
Keywords: Bezoars; Coca-Cola; Gastroscopy; Lithotripsy; Solubility.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tannin-phytobezoars with Gastric Outlet Obstruction Treated by Dissolution with Administration and Endoscopic Injection of Coca-Cola®, Endoscopic Crushing, and Removal (with Video).Intern Med. 2022 Feb 1;61(3):335-338. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8090-21. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34334573 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review: Coca-Cola can effectively dissolve gastric phytobezoars as a first-line treatment.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jan;37(2):169-73. doi: 10.1111/apt.12141. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23252775
-
How good is cola for dissolution of gastric phytobezoars?World J Gastroenterol. 2009 May 14;15(18):2265-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2265. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19437568 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Coca-Cola on the Dissolution of Persimmon-Related Phytobezoar in a Tertiary Care Hospital.Cureus. 2024 Feb 18;16(2):e54420. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54420. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38510864 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric Outlet Obstruction--An Unexpected Complication during Coca-Cola Therapy for a Gastric Bezoar: A Case Report and Literature Review.Intern Med. 2016;55(9):1085-9. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.5567. Epub 2016 May 1. Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27150859 Review.
Cited by
-
Has Coca-Cola treatment become the first-line therapy for gastric bezoars, both in general and specifically for western countries?World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 May 16;16(5):237-243. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i5.237. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38813574 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approach to managing two enormous bezoars with successive snare-tip electrocautery: A case report.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Jan 16;17(1):102185. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.102185. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39850916 Free PMC article.
-
A giant fecaloma causing stercoral colitis secondary to aripiprazole and benztropine: A case report.Qatar Med J. 2025 Jul 5;2025(2):58. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2025.58. eCollection 2025. Qatar Med J. 2025. PMID: 40792242 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric Bezoars: A Retrospective Analysis of 44 Cases.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Aug 28;30:e945377. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945377. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39192566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu X, Guo Q, Xu QW, Zhang RY, Yang YC, Han SX, Liu WH. Novel endoscopic tangential sawing technique in treatment of giant gastric bezoars: a retrospective single-center study (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;96:150–154. - PubMed
-
- Ladas SD, Kamberoglou D, Karamanolis G, Vlachogiannakos J, Zouboulis-Vafiadis I. Systematic review: Coca-Cola can effectively dissolve gastric phytobezoars as a first-line treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;37:169–173. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

