Association between triglyceride-glucose index and colorectal polyps: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38464818
- PMCID: PMC10921154
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i2.55
Association between triglyceride-glucose index and colorectal polyps: A retrospective cross-sectional study
Retraction in
-
Retraction note to: Association between triglyceride-glucose index and colorectal polyps: A retrospective cross-sectional study.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):500-501. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i8.500. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024. PMID: 39155998 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Colorectal polyps (CPs) are frequently occurring abnormal growths in the colorectum, and are a primary precursor of colorectal cancer (CRC). The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a novel marker that assesses metabolic health and insulin resistance, and has been linked to gastrointestinal cancers.
Aim: To investigate the potential association between the TyG index and CPs, as the relation between them has not been documented.
Methods: A total of 2537 persons undergoing a routine health physical examination and colonoscopy at The First People's Hospital of Kunshan, Jiangsu Province, China, between January 2020 and December 2022 were included in this retrospective cross-sectional study. After excluding individuals who did not meet the eligibility criteria, descriptive statistics were used to compare characteristics between patients with and without CPs. Logistic regression analyses were conducted to determine the associations between the TyG index and the prevalence of CPs. The TyG index was calculated using the following formula: Ln [triglyceride (mg/dL) × glucose (mg/dL)/2]. The presence and types of CPs was determined based on data from colonoscopy reports and pathology reports.
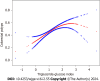
Results: A nonlinear relation between the TyG index and the prevalence of CPs was identified, and exhibited a curvilinear pattern with a cut-off point of 2.31. A significant association was observed before the turning point, with an odds ratio (95% confidence interval) of 1.70 (1.40, 2.06), P < 0.0001. However, the association between the TyG index and CPs was not significant after the cut-off point, with an odds ratio (95% confidence interval) of 0.57 (0.27, 1.23), P = 0.1521.
Conclusion: Our study revealed a curvilinear association between the TyG index and CPs in Chinese individuals, suggesting its potential utility in developing colonoscopy screening strategies for preventing CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Colorectal polyps; Cross-sectional study; Insulin resistance; Triglyceride-glucose index.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declared no conflict-of-interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) is a predictor of incident colorectal cancer: a population-based longitudinal study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2020 Jul 24;20(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00581-w. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020. PMID: 32709256 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear association between the triglyceride-glucose index and diabetes mellitus in overweight and obese individuals: a cross-sectional retrospective analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Aug 8;16(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01434-5. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39118153 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and cognitive impairment in China: a community population-based cross-sectional study.Nutr Neurosci. 2024 Apr;27(4):342-352. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2023.2193765. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Nutr Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 36976719
-
Inverted U-shaped association between the systemic immune-inflammation index and colorectal polyps in Chinese patients: a cross-sectional study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 27;11:1515230. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1515230. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39931434 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride glucose index and obstructive sleep apnea risk in Korean adults: a cross-sectional cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Aug 8;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01358-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32771021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retraction note to: Association between triglyceride-glucose index and colorectal polyps: A retrospective cross-sectional study.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):500-501. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i8.500. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024. PMID: 39155998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meseeha M, Attia M. Colon Polyps. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2017;66:683–691. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources