Development and validation of a diagnostic nomogram to evaluate tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis of IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 38464822
- PMCID: PMC10920839
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.91804
Development and validation of a diagnostic nomogram to evaluate tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis of IgA nephropathy
Abstract
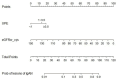
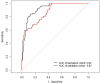
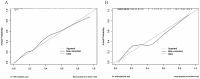
Background: IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is a cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis is associated with IgAN prognosis. However, simple tools for predicting pathological lesions of IgAN remain limited. Our objective was to develop a tool for evaluating tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis in patients with IgAN. Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 410 biopsy-verified IgAN patients were included. The factors associated with the incident interstitial fibrosis or tubular atrophy in IgAN were confirmed by using logistic regression analysis. A nomogram was developed using logistic regression coefficients to evaluate tubular atrophy or interstitial fibrosis. Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) and calibration curves were used to determine the discriminative ability and predictive accuracy of the nomogram. Results: In this study, the IgAN patients with tubular atrophy or interstitial fibrosis were older and had a higher percentage of males, hypertension and urinary protein excretion (UPE), with high levels of serum cystatin C, serum creatinine, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and serum C4. The eGFRcr-cys equation calculated using serum creatinine, cystatin C and UPE were considered independent influencing factors of tubular atrophy or interstitial fibrosis in patients with IgAN. Furthermore, the nomogram demonstrated good discrimination (AUC: 0.87, 95% CI 0.81 to 0.93) and calibration in the validation cohort. Conclusion: The eGFRcr-cys and UPE are associated with tubular atrophy or interstitial fibrosis in patients with IgAN. Diagnostic nomogram can predict tubular atrophy or interstitial fibrosis in IgAN.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; estimated glomerular filtration rate; nomogram; pathological change.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between blood neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and renal tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jun;35(6):e23774. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23774. Epub 2021 May 5. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33951240 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary probabilistic nomogram model for predicting renal arteriolar damage in IgA nephropathy from clinical parameters.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 1;15:1435838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1435838. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39011045 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperuricemia and hypertriglyceridemia indicate tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis in patients with IgA nephropathy and membranous nephropathy.Int Urol Nephrol. 2021 Nov;53(11):2321-2332. doi: 10.1007/s11255-021-02844-4. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33895976
-
Immunoglobulin a nephropathy: Pathological markers of renal survival in paediatric patients.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Dec;21(12):995-1002. doi: 10.1111/nep.12850. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 27414046 Review.
-
Immunoglobulin A nephropathy in association with inflammatory bowel diseases: results from a national study and systematic literature review.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 Feb 25;37(3):531-539. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa378. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022. PMID: 33416845
References
-
- D'Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987;64:709–27. - PubMed
-
- Schena FP, Cerullo G, Rossini M, Lanzilotta SG, D'Altri C, Manno C. Increased risk of end-stage renal disease in familial IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:453–60. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico G. Natural history of idiopathic IgA nephropathy and factors predictive of disease outcome. Semin Nephrol. 2004;24:179–96. - PubMed
-
- Chen T, Li X, Li Y, Xia E, Qin Y, Liang S. et al. Prediction and Risk Stratification of Kidney Outcomes in IgA Nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74:300–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

