Oridonin inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition of laryngeal carcinoma by positively regulating LKB1/AMPK signaling
- PMID: 38464825
- PMCID: PMC10920846
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.92182
Oridonin inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition of laryngeal carcinoma by positively regulating LKB1/AMPK signaling
Abstract
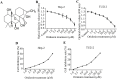
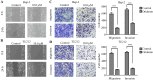
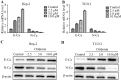
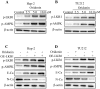
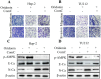
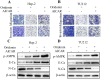
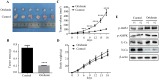
Oridonin is the main bioactive component of Rabdosia rubescens, and its anticancer activity has been reported in a variety of cancers. However, the molecular mechanism of oridonin in laryngeal carcinoma remains unclear. In the present study, the cytotoxic effect of oridonin on laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 and TU212 cell lines were initially detected by modified MTT assay. The results showed that oridonin had a dose-dependent anti-proliferative effect on laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 and TU212 cells. Next, we found that oridonin significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of human laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 and TU212 cell lines by wound healing assay and transwell assay. Subsequently, the results of quantitative real-time PCR assay and western blotting assay confirmed that oridonin upregulated the expression of E-cadherin while downregulated the expression of N-cadherin in a concentration-dependent manner at mRNA and protein levels. In addition, phosphorylation levels of liver kinase B1 (p-LKB1) and AMP-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) were also elevated upon oridonin treatment. To further verify the role of LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway in laryngeal carcinoma, overexpression of LKB1 was constructed by plasmid transfection. The data exhibited that overexpression of LKB1 could further reinforce the increase of E-cadherin level and decrease of N-cadherin level mediated by oridonin. Additionally, AMPK inhibitor compound C could reverse anti-metastatic effect of oridonin on laryngeal carcinoma, and antagonise EMT expression. In contrast, AMPK activator AICAR presented the opposite effect. In conclusion, our study revealed that oridonin could remarkably reverse the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of laryngeal carcinoma by positively regulating LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway, which suggested that oridonin may be a potential candidate for the treatment of laryngeal carcinoma in the future.
Keywords: AMPK; EMT; LKB1; Laryngeal carcinoma; Oridonin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang ZM, Zhao Z, Chen ZX. Impact of laryngocarcinoma at different sites in 16,255 individuals. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021: 1549782115. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa C, Mori N. The anti-malaria agent artesunate exhibits cytotoxic effects in primary effusion lymphoma. Invest New Drugs. 2021;39:111–21. - PubMed
-
- Obid R, Redlich M, Tomeh C. The treatment of laryngeal cancer. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2019;31:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Mai JH, Ma LG. [Human papillomavirus and laryngeal cancer] Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;54:385–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

