PKM2 interacts with and phosphorylates PHB2 to sustain mitochondrial quality control against septic cerebral-cardiac injury
- PMID: 38464826
- PMCID: PMC10920845
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.92367
PKM2 interacts with and phosphorylates PHB2 to sustain mitochondrial quality control against septic cerebral-cardiac injury
Abstract
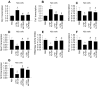
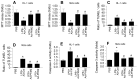
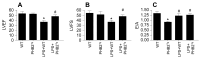
Sepsis induces profound disruptions in cellular homeostasis, particularly impacting mitochondrial function in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems. This study elucidates the regulatory role of the Pyruvate Kinase M2 (PKM2)- Prohibitin 2 (PHB2) axis in mitochondrial quality control during septic challenges and its protective effects against myocardial and cerebral injuries. Employing LPS-induced mouse models, we demonstrate a significant downregulation of PKM2 and PHB2 in both heart and brain tissues post-sepsis, with corresponding impairments in mitochondrial dynamics, including fission, fusion, and mitophagy. Overexpression of PKM2 and PHB2 not only restores mitochondrial function, as evidenced by normalized ATP production and membrane potential but also confers resistance to oxidative stress by mitigating reactive oxygen species generation. These cellular mechanisms translate into substantial in vivo benefits, with transgenic mice overexpressing PKM2 or PHB2 displaying remarkable resistance to sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte and neuronal apoptosis, and organ dysfunction. Our findings highlight the PKM2-PHB2 interaction as a novel therapeutic target for sepsis, providing a foundation for future research into mitochondrial-based interventions to treat this condition. The study's insights into the molecular underpinnings of sepsis-induced organ failure pave the way for potential clinical applications in the management of sepsis and related pathologies.
Keywords: PHB2; PKM2; mitochondrial quality control; septic cerebrovascular damage.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
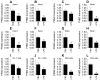
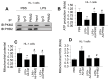
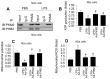
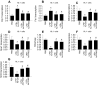
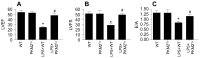
Similar articles
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 sustains cardiac mitochondrial quality surveillance in septic cardiomyopathy by regulating prohibitin 2 abundance via S91 phosphorylation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jun 10;81(1):254. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05253-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38856931 Free PMC article.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 sustains cardiac mitochondrial integrity in septic cardiomyopathy by regulating PHB2-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Apr 8;21(6):983-993. doi: 10.7150/ijms.94577. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38774750 Free PMC article.
-
Pgam5 aggravates hyperglycemia-induced myocardial dysfunction through disrupting Phb2-dependent mitochondrial dynamics.Int J Med Sci. 2024 May 5;21(7):1194-1203. doi: 10.7150/ijms.92872. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38818468 Free PMC article.
-
Review on the Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Septic Encephalopathy.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Mar;83(1):135-145. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01493-5. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39212823 Review.
-
The Role of PKM2 in the Regulation of Mitochondrial Function: Focus on Mitochondrial Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, Dynamic, and Apoptosis. PKM2 in Mitochondrial Function.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 6;2022:7702681. doi: 10.1155/2022/7702681. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35571239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lorenzana-Carrillo MA, Gopal K, Byrne NJ, Tejay S, Saleme B, Das SK. et al. TRIM35-mediated degradation of nuclear PKM2 destabilizes GATA4/6 and induces P53 in cardiomyocytes to promote heart failure. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14:eabm3565. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

