Validation of the Openwater wearable optical system: cerebral hemodynamic monitoring during a breath-hold maneuver
- PMID: 38464864
- PMCID: PMC10923543
- DOI: 10.1117/1.NPh.11.1.015008
Validation of the Openwater wearable optical system: cerebral hemodynamic monitoring during a breath-hold maneuver
Abstract
Significance: Bedside cerebral blood flow (CBF) monitoring has the potential to inform and improve care for acute neurologic diseases, but technical challenges limit the use of existing techniques in clinical practice.
Aim: Here, we validate the Openwater optical system, a novel wearable headset that uses laser speckle contrast to monitor microvascular hemodynamics.
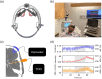
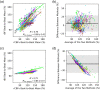
Approach: We monitored 25 healthy adults with the Openwater system and concurrent transcranial Doppler (TCD) while performing a breath-hold maneuver to increase CBF. Relative blood flow (rBF) was derived from changes in speckle contrast, and relative blood volume (rBV) was derived from changes in speckle average intensity.
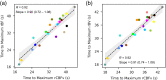
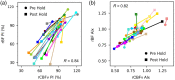
Results: A strong correlation was observed between beat-to-beat optical rBF and TCD-measured cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFv), ; the slope of the linear fit indicates good agreement, 0.87 (95% CI: 0.83 ). Beat-to-beat rBV and CBFv were also strongly correlated, , but as expected the two variables were not proportional; changes in rBV were smaller than CBFv changes, with linear fit slope of 0.18 (95% CI: 0.17 to 0.19). Further, strong agreement was found between rBF and CBFv waveform morphology and related metrics.
Conclusions: This first in vivo validation of the Openwater optical system highlights its potential as a cerebral hemodynamic monitor, but additional validation is needed in disease states.
Keywords: biomedical optics; breath-hold index; cerebral blood flow; cerebral hemodynamics; laser speckle contrast.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures




Update of
-
Validation of the Openwater wearable optical system: cerebral hemodynamic monitoring during a breath hold maneuver.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 12:2023.10.11.23296612. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.11.23296612. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Neurophotonics. 2024 Jan;11(1):015008. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.11.1.015008. PMID: 37873126 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Herscovitch P., Markham J., Raichle M. E., “Brain blood flow measured with intravenous . I. Theory and error analysis,” J. Nucl. Med. 24(9), 782–789 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Raichle M. E., et al. , “Brain blood flow measured with intravenous . II. Implementation and validation,” J. Nucl. Med. 24(9), 790–798 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Cenic A., et al. , “Dynamic CT measurement of cerebral blood flow: a validation study,” AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 20(1), 63–73 (1999). - PubMed

