Efficacy and Safety of High-Voltage Pulsed Radiofrequency versus Standard-Voltage Pulsed Radiofrequency for Patients with Neuropathic Pain: A Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38464903
- PMCID: PMC10922952
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S439909
Efficacy and Safety of High-Voltage Pulsed Radiofrequency versus Standard-Voltage Pulsed Radiofrequency for Patients with Neuropathic Pain: A Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic pain (NP) is recognized as one of the most difficult pain syndromes which lacks a safe, well-tolerated and effective treatment. Pulsed radiofrequency (PRF), a novel and minimally invasive interventions, has been introduced to alleviate various types of NP. Previous studies reported PRF with higher voltage could further improve the treatment efficacy. Therefore, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to determine whether high-voltage PRF is superior to standard-voltage PRF for the treatment of NP patients.
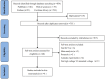
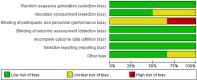
Methods: Databases published from the date of inception until 15 March 2022 on PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library were searched for RCTs comparing high-voltage PRF and standard-voltage PRF in NP patients. The primary outcome measures were the efficiency rates of NP patients with high-voltage PRF or standard-voltage PRF treatment. Data analysis was conducted using the Review Manager software (RevMan V.5.3).
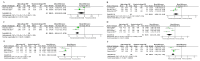
Results: Six RCTs involving 423 patients were included in our meta-analysis. Compared with standard-voltage PRF group, the high-voltage PRF group attained a higher efficiency rate at 1 month (P = 0.04; I2 = 0%), 3 months (P = 0.04; I2 = 0%), 6 months (P = 0.002; I2 = 0%) post-procedure respectively. There was no significant difference in the complications between the two groups.
Conclusion: Our study supported that high-voltage PRF attained more satisfactory efficacy than standard-voltage PRF without increased side effects. High-voltage PRF could be a promising, effective, minimally invasive technology for NP patients.
Keywords: efficacy; high-voltage; pulsed radiofrequency; standard-voltage; trigeminal neuralgia.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest in this work.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

