Autoimmune hepatitis-primary biliary cholangitis overlap syndrome complicated by various autoimmune diseases: A case report
- PMID: 38464929
- PMCID: PMC10921307
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1174
Autoimmune hepatitis-primary biliary cholangitis overlap syndrome complicated by various autoimmune diseases: A case report
Abstract
Background: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) are two common clinical autoimmune liver diseases, and some patients have both diseases; this feature is called AIH-PBC overlap syndrome. Autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) is the most frequently overlapping extrahepatic autoimmune disease. Immunoglobulin (IgG) 4-related disease is an autoimmune disease recognized in recent years, characterized by elevated serum IgG4 levels and infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells in tissues.
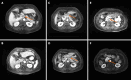
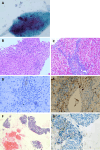
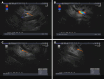
Case summary: A 68-year-old female patient was admitted with a history of right upper quadrant pain, anorexia, and jaundice on physical examination. Laboratory examination revealed elevated liver enzymes, multiple positive autoantibodies associated with liver and thyroid disease, and imaging and biopsy suggestive of pancreatitis, hepatitis, and PBC. A diagnosis was made of a rare and complex overlap syndrome of AIH, PBC, AITD, and IgG4-related disease. Laboratory features improved on treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid, methylprednisolone, and azathioprine.
Conclusion: This case highlights the importance of screening patients with autoimmune diseases for related conditions.
Keywords: Autoimmune hepatitis; Autoimmune thyroid disease; Case report; Overlap syndrome; Primary biliary cholangitis; Primary sclerosing cholangitis.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

