An Assessment of Trends in HIV-1 Prevalence and Incidence and Spatio-Temporal Analyses of HIV-1 Recent Infection Among MSM During the Surveillance Period Between 2018 and 2022 in Sichuan, China
- PMID: 38464995
- PMCID: PMC10924877
- DOI: 10.2147/HIV.S448096
An Assessment of Trends in HIV-1 Prevalence and Incidence and Spatio-Temporal Analyses of HIV-1 Recent Infection Among MSM During the Surveillance Period Between 2018 and 2022 in Sichuan, China
Abstract
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM) is one main type of high-risk activities facilitating HIV-1 transmission in Sichuan province. Previous works on HIV-1 incidence and prevalence among MSM only concentrated before 2018, the situation after that is unknown. In addition, the distribution of hot-spots related to current HIV-1 epidemic is also rarely known among MSM in Sichuan.
Objective: To update trends of HIV-1 prevalence and incidence and to visualize hot-spots of ongoing transmission in Sichuan province during surveillance period among MSM between 2018 and 2022.
Methods: Limiting Antigen Avidity assay was performed to detect recent infection within new HIV-1 diagnoses founded during surveillance period among MSM. The HIV-1 prevalence and incidence were calculated according to an extrapolation method proposed by publications and guidelines. Trend tests were performed using χ2 tests with linear-by-linear association. The spatial analysis was conducted with ArcGIS 10.7 to figure hot-spots of HIV-1 recent infections among MSM.
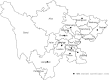
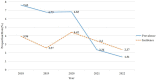
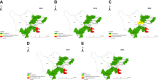
Results: Between 2018 and 2022, 16,697 individuals participated in HIV-1 MSM sentinel surveillance program, of which 449 samples (98.25%) were tested with LAg-Avidity EIA, and 230 samples were classified as recent infection. Respectively, the overall prevalence and incidence were 2.74% and 3.69% (95% CI: 3.21, 4.16) and both had significant declining trends (p < 0.001). Luzhou city had a highest HIV-1 incidence (10.74%, 95% CI: 8.39, 13.10) over the study period and was recognized as a hot-spot for recent HIV-1 infection among MSM.
Conclusion: During the surveillance period, both HIV-1 prevalence and incidence were declining. However, Luzhou city had an unusually high HIV-1 incidence and became an emerging hot-spot of recent HIV-1 infection among MSM. This finding suggested focused attention, cross-regional intervention strategies, and prevention programs are urgently required to curb the spread of ongoing transmission.
Keywords: HIV-1 recent infection; hot-spots; human immunodeficiency virus type 1; incidence; men who have sex with men.
© 2024 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Demographic Characteristics and Hot-Spot Areas of Recent Infections Among New HIV Diagnoses in Sichuan, China, Between 2018 and 2020.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Feb 5;16:779-789. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S394828. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36779044 Free PMC article.
-
The Update of HIV-1 Prevalence and Incidence and Spatio-Temporal Analyses of HIV Recent Infection Among Four Sub-Groups in Sichuan, China During Surveillance Period Between 2016 and 2022.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Oct 4;16:6535-6548. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S428744. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37814665 Free PMC article.
-
[Performance of limiting-antigen avidity enzyme immunoassay and pooling PCR in detection of recent HIV-1 infection among men who have sex with men in Yunnan province].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Apr 10;42(4):706-710. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200605-00810. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34814455 Chinese.
-
Distributions and trends in sexual behaviors and HIV incidence among men who have sex with men in China.BMC Public Health. 2012 Jul 24;12:546. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-546. BMC Public Health. 2012. PMID: 22828173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in HIV prevalence among men who have sex with men in China 2003-09: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sex Health. 2013 Jul;10(3):211-9. doi: 10.1071/SH12093. Sex Health. 2013. PMID: 23611402
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

