Reciprocal regulation of SIRT1 and AMPK by Ginsenoside compound K impedes the conversion from plasma cells to mitigate for podocyte injury in MRL/ lpr mice in a B cell-specific manner
- PMID: 38465215
- PMCID: PMC10920007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.11.006
Reciprocal regulation of SIRT1 and AMPK by Ginsenoside compound K impedes the conversion from plasma cells to mitigate for podocyte injury in MRL/ lpr mice in a B cell-specific manner
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to 'Reciprocal regulation of SIRT1 and AMPK by Ginsenoside compound K impedes the conversion from plasma cells to mitigate for podocyte injury in MRL/lpr mice in a B cell-specific manner' [J Ginseng Res Volume 48 (2024) 190-201/JGR-D-23-00097].J Ginseng Res. 2025 Mar;49(2):223. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.12.006. Epub 2024 Dec 21. J Ginseng Res. 2025. PMID: 40061480 Free PMC article.
Abstract
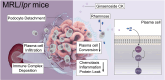
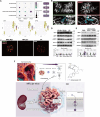
Background: Deposition of immune complexes drives podocyte injury acting in the initial phase of lupus nephritis (LN), a process mediated by B cell involvement. Accordingly, targeting B cell subsets represents a potential therapeutic approach for LN. Ginsenoside compound K (CK), a bioavailable component of ginseng, possesses nephritis benefits in lupus-prone mice; however, the underlying mechanisms involving B cell subpopulations remain elusive.
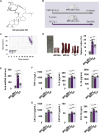
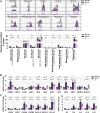
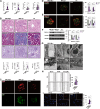
Methods: Female MRL/lpr mice were administered CK (40 mg/kg) intragastrically for 10 weeks, followed by measurements of anti-dsDNA antibodies, inflammatory chemokines, and metabolite profiles on renal samples. Podocyte function and ultrastructure were detected. Publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing data and flow cytometry analysis were employed to investigate B cell subpopulations. Metabolomics analysis was adopted. SIRT1 and AMPK expression were analyzed by immunoblotting and immunofluorescence assays.
Results: CK reduced proteinuria and protected podocyte ultrastructure in MRL/lpr mice by suppressing circulating anti-dsDNA antibodies and mitigating systemic inflammation. It activated B cell-specific SIRT1 and AMPK with Rhamnose accumulation, hindering the conversion of renal B cells into plasma cells. This cascade facilitated the resolution of local renal inflammation. CK facilitated the clearance of deposited immune complexes, thus reinstating podocyte morphology and mobility by normalizing the expression of nephrin and SYNPO.
Conclusions: Our study reveals the synergistic interplay between SIRT1 and AMPK, orchestrating the restoration of renal B cell subsets. This process effectively mitigates immune complex deposition and preserves podocyte function. Accordingly, CK emerges as a promising therapeutic agent, potentially alleviating the hyperactivity of renal B cell subsets during LN.
Keywords: Ginsenoside CK; Lupus nephritis; Plasma cell; Podocyte.
© 2024 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Compound K Mitigates Mitochondrial Fission Through Bile Acid Receptors/YAP Signaling to Counteract Podocyte Injury in Lupus Nephritis.Phytother Res. 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8492. Online ahead of print. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 40528637
-
Corrigendum to 'Reciprocal regulation of SIRT1 and AMPK by Ginsenoside compound K impedes the conversion from plasma cells to mitigate for podocyte injury in MRL/lpr mice in a B cell-specific manner' [J Ginseng Res Volume 48 (2024) 190-201/JGR-D-23-00097].J Ginseng Res. 2025 Mar;49(2):223. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.12.006. Epub 2024 Dec 21. J Ginseng Res. 2025. PMID: 40061480 Free PMC article.
-
Fasudil compensates podocyte injury via CaMK4/Rho GTPases signal and actin cytoskeleton-dependent activation of YAP in MRL/lpr mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jun;119:110199. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110199. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37094544
-
Unraveling the podocyte injury in lupus nephritis: Clinical and experimental approaches.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2017 Apr;46(5):632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2017. PMID: 27839739 Review.
-
Anticancer Mechanisms of Ginsenoside Compound K: A Review.Diseases. 2025 May 5;13(5):143. doi: 10.3390/diseases13050143. Diseases. 2025. PMID: 40422575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The lactylation-immune regulatory axis: a potential therapeutic target for migraine prevention and treatment.J Headache Pain. 2025 Jun 4;26(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02075-3. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40468199 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells.Open Life Sci. 2025 Apr 25;20(1):20221038. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-1038. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40291778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin F., Chan A.C. B cell immunobiology in disease: evolving concepts from the clinic. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:467–496. - PubMed
-
- Gregersen J.W., Jayne D.R. B-cell depletion in the treatment of lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:505–514. - PubMed
-
- Murphy G., Isenberg D.A. New therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus – past imperfect, future tense. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:403–412. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

