Mass spectrometry-based ginsenoside profiling: Recent applications, limitations, and perspectives
- PMID: 38465223
- PMCID: PMC10920005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.01.004
Mass spectrometry-based ginsenoside profiling: Recent applications, limitations, and perspectives
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to Mass spectrometry-based ginsenoside profiling: Recent applications, limitations, and perspectives [J. Ginseng Res. 48(2) (2024) 149-162].J Ginseng Res. 2024 Nov;48(6):628. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.09.004. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 39583166 Free PMC article.
Abstract
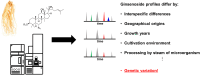
Ginseng, the roots of Panax species, is an important medicinal herb used as a tonic. As ginsenosides are key bioactive components of ginseng, holistic chemical profiling of them has provided many insights into understanding ginseng. Mass spectrometry has been a major methodology for profiling, which has been applied to realize numerous goals in ginseng research, such as the discrimination of different species, geographical origins, and ages, and the monitoring of processing and biotransformation. This review summarizes the various applications of ginsenoside profiling in ginseng research over the last three decades that have contributed to expanding our understanding of ginseng. However, we also note that most of the studies overlooked a crucial factor that influences the levels of ginsenosides: genetic variation. To highlight the effects of genetic variation on the chemical contents, we present our results of untargeted and targeted ginsenoside profiling of different genotypes cultivated under identical conditions, in addition to data regarding genome-level genetic diversity. Additionally, we analyze the other limitations of previous studies, such as imperfect variable control, deficient metadata, and lack of additional effort to validate causation. We conclude that the values of ginsenoside profiling studies can be enhanced by overcoming such limitations, as well as by integrating with other -omics techniques.
Keywords: Chemical profiling; Genetic variation; Ginseng; Ginsenoside; Mass spectrometry.
© 2024 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mass Spectrometry Based Profiling and Imaging of Various Ginsenosides from Panax ginseng Roots at Different Ages.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 24;18(6):1114. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061114. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28538661 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic profiling reveals MEP pathway contributing to ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng.BMC Genomics. 2019 May 17;20(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5718-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31101014 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of multiplatform metabolomics and multivariate analysis for geographical origin discrimination of Panax ginseng.Food Res Int. 2022 Sep;159:111610. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111610. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35940805
-
Diversity of Ginsenoside Profiles Produced by Various Processing Technologies.Molecules. 2020 Sep 24;25(19):4390. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194390. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32987784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3452. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153452. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751233 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kitagawa I., Taniyama T., Yoshikawa M., Ikenishi Y., Nakagawa Y. Chemical studies on crude drug processing. VI.: chemical structures of malonyl-ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, and Rd isolated from the root of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Chem Pharm Bull. 1989;37:2961–2970.
-
- Liu Z., Li Y., Li X., Ruan C.-C., Wang L.-J., Sun G.-Z. The effects of dynamic changes of malonyl ginsenosides on evaluation and quality control of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;64–65:56–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

