Clinical Trials That Have Changed Obstetric Practice: The Chronic Hypertension and Pregnancy (CHAP) Trial
- PMID: 38465909
- PMCID: PMC11062801
- DOI: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000857
Clinical Trials That Have Changed Obstetric Practice: The Chronic Hypertension and Pregnancy (CHAP) Trial
Abstract
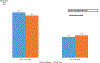
We describe the evolution of treatment recommendations for chronic hypertension (CHTN) in pregnancy, the CHTN and pregnancy (CHAP) trial, and its impact on obstetric practice. The US multicenter CHAP trial showed that antihypertensive treatment for mild CHTN in pregnancy [blood pressures (BP)<160/105 mm Hg] to goal<140/90 mm Hg, primarily with labetalol or nifedipine compared with no treatment unless BP were severe reduced the composite risk of superimposed severe preeclampsia, indicated preterm birth <35 weeks, placental abruption, and fetal/neonatal death. As a result of this trial, professional societies in the United States recommended treatment of patients with CHTN in pregnancy to BP goal<140/90 mm Hg.
Copyright © 2024 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
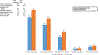
Similar articles
-
Pregnancy Outcomes of Nifedipine Compared With Labetalol for Oral Treatment of Mild Chronic Hypertension.Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Jul 1;144(1):126-134. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000005613. Epub 2024 May 23. Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38949541 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mean Arterial Pressure and Neonatal Outcomes in Pregnancies Complicated by Mild Chronic Hypertension.Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Jul 1;144(1):101-108. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000005611. Epub 2024 May 23. Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38781591 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral beta-blockers for mild to moderate hypertension during pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;2003(4):CD002863. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002863. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002863. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002863. PMID: 11034777 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of dual alpha and beta blockers for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Aug 26;2015(8):CD007449. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007449.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26306578 Free PMC article.
-
Oral nifedipine versus intravenous labetalol for severe hypertension during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):40-7. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.13463. Epub 2015 Jun 26. BJOG. 2016. PMID: 26113232
Cited by
-
Exploring Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Approaches to Managing Hypertension During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Dec 11;16(12):e75534. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75534. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. Retraction in: Cureus. 2025 Apr 1;17(4):r172. doi: 10.7759/cureus.r172. PMID: 39803125 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE, Collins KJ, Himmelfarb CD, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):E13–E115. - PubMed
-
- Ananth CV, Duzyj CM, Yadava S, Schwebel M, Tita ATN, Joseph KS. Changes in the prevalence of chronic hypertension in pregnancy, United States, 1970 to 2010.Hypertension. 2019; 74:1089–1095 - PubMed
-
- Garovic VD, Dechend R, Easterling T, Karumanchi SA, McMurtry Baird S, Magee LA, Rana S, Vermunt JV, August P; American Heart Association Council on Hypertension; Council on the Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, Kidney in Heart Disease Science Committee; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; and Stroke Council. Hypertension in Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Blood Pressure Goals, and Pharmacotherapy: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2022. Feb;79(2):e21–e41. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000208. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Erratum in: Hypertension. 2022 Mar;79(3):e70. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

