Paxillin phase separation promotes focal adhesion assembly and integrin signaling
- PMID: 38466167
- PMCID: PMC10926639
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202209027
Paxillin phase separation promotes focal adhesion assembly and integrin signaling
Abstract
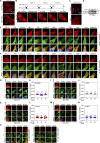
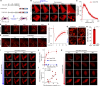
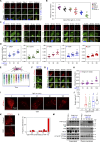
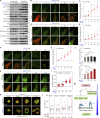
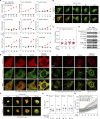
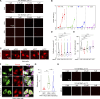
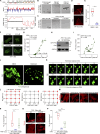
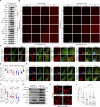
Focal adhesions (FAs) are transmembrane protein assemblies mediating cell-matrix connection. Although protein liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) has been tied to the organization and dynamics of FAs, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we experimentally tune the LLPS of PXN/Paxillin, an essential scaffold protein of FAs, by utilizing a light-inducible Cry2 system in different cell types. In addition to nucleating FA components, light-triggered PXN LLPS potently activates integrin signaling and subsequently accelerates cell spreading. In contrast to the homotypic interaction-driven LLPS of PXN in vitro, PXN condensates in cells are associated with the plasma membrane and modulated by actomyosin contraction and client proteins of FAs. Interestingly, non-specific weak intermolecular interactions synergize with specific molecular interactions to mediate the multicomponent condensation of PXN and are efficient in promoting FA assembly and integrin signaling. Thus, our data establish an active role of the PXN phase transition into a condensed membrane-associated compartment in promoting the assembly/maturation of FAs.
© 2024 Liang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An ULK1/2-PXN mechanotransduction pathway suppresses breast cancer cell migration.EMBO Rep. 2023 Nov 6;24(11):e56850. doi: 10.15252/embr.202356850. Epub 2023 Oct 17. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37846507 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of substrate stiffness and actomyosin contractility on coupling between force transmission and vinculin-paxillin recruitment at single focal adhesions.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jul 7;28(14):1901-1911. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-02-0116. Epub 2017 May 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28468976 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of the target-binding mode of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein in the regulation of focal adhesion dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 12;294(15):5827-5839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006915. Epub 2019 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30737283 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesions function as a mechanosensor.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;126:55-73. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394624-9.00003-8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014. PMID: 25081614 Review.
-
Assembly and mechanosensory function of focal adhesions: experiments and models.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;85(3-4):165-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.11.001. Epub 2005 Dec 19. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16360240 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological functions of ULK1/2.J Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 1;436(15):168472. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168472. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38311233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Vascular Injury and Repair by P21-Activated Kinase 1 and P21-Activated Kinase 2: Therapeutic Potential and Challenges.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 13;14(12):1596. doi: 10.3390/biom14121596. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G3BP1 ribonucleoprotein complexes regulate focal adhesion protein mobility and cell migration.Cell Rep. 2025 Feb 25;44(2):115237. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115237. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 39883578 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Insights Into Electroacupuncture Using Different Acupoint Combinations to Repair Mucosal Inflammatory Injury Induced in a Rat Model of Gastric Ulcer.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 11;18:3399-3417. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S504930. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40093956 Free PMC article.
-
An ULK1/2-PXN mechanotransduction pathway suppresses breast cancer cell migration.EMBO Rep. 2023 Nov 6;24(11):e56850. doi: 10.15252/embr.202356850. Epub 2023 Oct 17. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37846507 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

