Association between chiropractic spinal manipulation and cauda equina syndrome in adults with low back pain: Retrospective cohort study of US academic health centers
- PMID: 38466710
- PMCID: PMC10927125
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299159
Association between chiropractic spinal manipulation and cauda equina syndrome in adults with low back pain: Retrospective cohort study of US academic health centers
Abstract
Background: Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a lumbosacral surgical emergency that has been associated with chiropractic spinal manipulation (CSM) in case reports. However, identifying if there is a potential causal effect is complicated by the heightened incidence of CES among those with low back pain (LBP). The study hypothesis was that there would be no increase in the risk of CES in adults with LBP following CSM compared to a propensity-matched cohort following physical therapy (PT) evaluation without spinal manipulation over a three-month follow-up period.
Methods: A query of a United States network (TriNetX, Inc.) was conducted, searching health records of more than 107 million patients attending academic health centers, yielding data ranging from 20 years prior to the search date (July 30, 2023). Patients aged 18 or older with LBP were included, excluding those with pre-existing CES, incontinence, or serious pathology that may cause CES. Patients were divided into two cohorts: (1) LBP patients receiving CSM or (2) LBP patients receiving PT evaluation without spinal manipulation. Propensity score matching controlled for confounding variables associated with CES.
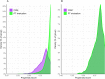
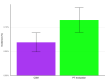
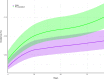
Results: 67,220 patients per cohort (mean age 51 years) remained after propensity matching. CES incidence was 0.07% (95% confidence intervals [CI]: 0.05-0.09%) in the CSM cohort compared to 0.11% (95% CI: 0.09-0.14%) in the PT evaluation cohort, yielding a risk ratio and 95% CI of 0.60 (0.42-0.86; p = .0052). Both cohorts showed a higher rate of CES during the first two weeks of follow-up.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that CSM is not a risk factor for CES. Considering prior epidemiologic evidence, patients with LBP may have an elevated risk of CES independent of treatment. These findings warrant further corroboration. In the meantime, clinicians should be vigilant to identify LBP patients with CES and promptly refer them for surgical evaluation.
Copyright: © 2024 Trager et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Robert J. Trager acknowledges that he has received royalties as the author of two texts on the topic of sciatica. The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chiropractic spinal manipulation and likelihood of tramadol prescription in adults with radicular low back pain: a retrospective cohort study using US data.BMJ Open. 2024 May 1;14(5):e078105. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078105. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38692725 Free PMC article.
-
Association between chiropractic spinal manipulation for sciatica and opioid-related adverse events: A retrospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 28;20(1):e0317663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317663. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39874372 Free PMC article.
-
Association between chiropractic spinal manipulation and gabapentin prescription in adults with radicular low back pain: retrospective cohort study using US data.BMJ Open. 2023 Jul 21;13(7):e073258. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073258. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37479505 Free PMC article.
-
Cauda Equina Syndrome Due to Vigorous Back Massage With Spinal Manipulation in a Patient With Pre-Existing Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Case Report and Literature Review.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018 Apr;97(4):e23-e26. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000809. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 28796647 Review.
-
Cauda equina syndrome in patients undergoing manipulation of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992 Dec;17(12):1469-73. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199212000-00005. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992. PMID: 1471004 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological and Pharmacological Treatments for Non-Acute Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Multicenter, Pragmatic, Randomized Controlled, Parallel-Grouped Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 12;14(4):1204. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041204. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004733 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

