Proteasome inhibition triggers tissue-specific immune responses against different pathogens in C. elegans
- PMID: 38466732
- PMCID: PMC10957088
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002543
Proteasome inhibition triggers tissue-specific immune responses against different pathogens in C. elegans
Abstract
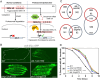
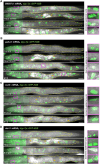
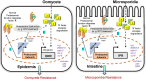
Protein quality control pathways play important roles in resistance against pathogen infection. For example, the conserved transcription factor SKN-1/NRF up-regulates proteostasis capacity after blockade of the proteasome and also promotes resistance against bacterial infection in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. SKN-1/NRF has 3 isoforms, and the SKN-1A/NRF1 isoform, in particular, regulates proteasomal gene expression upon proteasome dysfunction as part of a conserved bounce-back response. We report here that, in contrast to the previously reported role of SKN-1 in promoting resistance against bacterial infection, loss-of-function mutants in skn-1a and its activating enzymes ddi-1 and png-1 show constitutive expression of immune response programs against natural eukaryotic pathogens of C. elegans. These programs are the oomycete recognition response (ORR), which promotes resistance against oomycetes that infect through the epidermis, and the intracellular pathogen response (IPR), which promotes resistance against intestine-infecting microsporidia. Consequently, skn-1a mutants show increased resistance to both oomycete and microsporidia infections. We also report that almost all ORR/IPR genes induced in common between these programs are regulated by the proteasome and interestingly, specific ORR/IPR genes can be induced in distinct tissues depending on the exact trigger. Furthermore, we show that increasing proteasome function significantly reduces oomycete-mediated induction of multiple ORR markers. Altogether, our findings demonstrate that proteasome regulation keeps innate immune responses in check in a tissue-specific manner against natural eukaryotic pathogens of the C. elegans epidermis and intestine.
Copyright: © 2024 Grover et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mutations in nucleotide metabolism genes bypass proteasome defects in png-1/NGLY1-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jul 11;22(7):e3002720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002720. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38991033 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Sequence Editing of SKN-1A/Nrf1 by Peptide:N-Glycanase Controls Proteasome Gene Expression.Cell. 2019 Apr 18;177(3):737-750.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.035. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31002798 Free PMC article.
-
Protein sequence editing defines distinct and overlapping functions of SKN-1A/Nrf1 and SKN-1C/Nrf2.PLoS Genet. 2025 Jul 7;21(7):e1011780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011780. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40623109 Free PMC article.
-
SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):290-301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26232625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from C. elegans into Microsporidia Biology and Host-Pathogen Relationships.Exp Suppl. 2022;114:115-136. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-93306-7_5. Exp Suppl. 2022. PMID: 35544001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of Distinct Transcriptional Factors in the Innate Immunity of C. elegans.Cells. 2025 Feb 21;14(5):327. doi: 10.3390/cells14050327. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphism of Keratin Gene KRT71 and Its Relationship with Wool Properties in Gansu Alpine Fine-Wool Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;15(14):2028. doi: 10.3390/ani15142028. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723491 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and clinical implications of a model of surveillance immunity.J Clin Invest. 2025 Aug 1;135(15):e191645. doi: 10.1172/JCI191645. eCollection 2025 Aug 1. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40759580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf1 acts as a highly-conserved determinon for maintaining robust redox homeostasis in the eco-evo-devo process of life histories.Cell Stress. 2025 Jul 7;9:65-142. doi: 10.15698/cst2025.07.306. eCollection 2025. Cell Stress. 2025. PMID: 40703332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nervous system guides behavioral immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 15;12:e18289. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18289. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39430568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fasseas MK, Grover M, Drury F, Essmann CL, Kaulich E, Schafer WR, Barkoulas M. Chemosensory neurons modulate the response to oomycete recognition in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Rep. 2021;34(2):108604. Epub 2021/01/14. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108604 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7809619. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakowski MA, Desjardins CA, Smelkinson MG, Dunbar TL, Lopez-Moyado IF, Rifkin SA, et al.. Ubiquitin-mediated response to microsporidia and virus infection in C. elegans. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10(6):e1004200. Epub 20140619. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004200 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4063957. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

