Effect of metal artefact reduction level on the assessment of dental implant positioning by cone-beam computed tomography
- PMID: 38466923
- PMCID: PMC11056797
- DOI: 10.1093/dmfr/twae008
Effect of metal artefact reduction level on the assessment of dental implant positioning by cone-beam computed tomography
Abstract
Objectives: This study evaluated the effect of metal artefact reduction (MAR) level and tube current on the assessment of dental implant positioning relative to the mandibular canal (MC) through cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
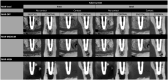
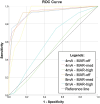
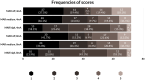
Methods: Titanium dental implants were placed in dried mandibles at 0.5-mm superior to the MC (group 1/n = 8) and 0.5-mm inside the MC with perforation of the cortex (group 2/n = 10). CBCT scans were obtained with different levels of MAR (off, medium, and high) and 2 tube currents (4 and 8 mA). Four examiners analysed the images and scored the contact between the implant and the MC using a 5-point scale. Sensitivity, specificity, area under receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), and frequency of scores were calculated. Data were compared with analysis of variance 2-way and Tukey's test and scores with Chi-square test.
Results: Specificity and area under ROC curve decreased significantly when MAR level was high compared with MAR-medium and MAR-off. The frequency of score 3 (inconclusive) was the highest, and scores 1 and 5 (definitely no contact and definitely contact, respectively) were the lowest with MAR-high, regardless of the tube current. When MAR was off, there were higher frequencies of scores 1 and 5.
Conclusions: The level of MAR influences the assessment of the relationship between the dental implant and the MC. MAR-high led to lower diagnostic accuracy compared with MAR-medium and off.
Advances in knowledge: This article shows that high level of MAR can interfere in the diagnostic of dental implant positioning relative to the MC, decreasing its accuracy.
Keywords: artefacts; cone-beam computed tomography; dental implant; mandibular canal; metal artefact reduction.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology and the International Association of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of metal artefact reduction on the diagnosis of contact between implant and mandibular canal in cone beam computed tomography: An ex-vivo study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2023 Jul;34(7):741-750. doi: 10.1111/clr.14100. Epub 2023 May 28. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2023. PMID: 37246310
-
Influence of tube current and metal artifact reduction on the diagnosis of external cervical resorption in teeth adjacent to a dental implant in CBCT: an ex-vivo study.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Jun 4;28(6):356. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05750-y. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38834721
-
Combining different metal artifact reduction levels with sharpening filters and slice thickness for the visualization of mandibular canals perforated by implants.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Nov 7;28(12):632. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-06031-4. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 39505740
-
Artefacts at different distances from titanium and zirconia implants in cone-beam computed tomography: effect of tube current and metal artefact reduction.Clin Oral Investig. 2021 Aug;25(8):5087-5094. doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-03821-y. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Clin Oral Investig. 2021. PMID: 33544197
-
Efficacy of two radiographic algorithms for detection of peri-implant bone defects on cone-beam computed tomography scans.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jan 7;25(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05397-x. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39773233 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and evaluation of a deep learning model to reduce exomass-related metal artefacts in cone-beam CT: an ex vivo study using porcine mandibles.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2025 Feb 1;54(2):109-117. doi: 10.1093/dmfr/twae062. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39589904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mozzo P, Procacci C, Tacconi A, Tinazzi Martini P, Bergamo Andreis IA.. A new volumetric CT machine for dental imaging based on the cone-beam technique: preliminary results. Eur Radiol. 1998;8(9):1558-1564. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs R, Quirynen M.. Dental cone beam computed tomography: justification for use in planning oral implant placement. Periodontol 2000. 2014;66(1):203-213. - PubMed
-
- Mahnken AH, Raupach R, Wildberger JE, et al.A new algorithm for metal artifact reduction in computed tomography: in vitro and in vivo evaluation after total hip replacement. Invest Radiol. 2003;38(12):769-775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

