Characterization of the intrahippocampal kainic acid model in female mice with a special focus on seizure suppression by antiseizure medications
- PMID: 38467356
- PMCID: PMC7615823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114749
Characterization of the intrahippocampal kainic acid model in female mice with a special focus on seizure suppression by antiseizure medications
Abstract
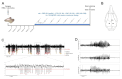
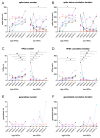
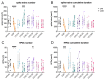
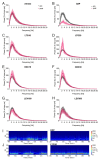
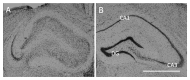
Despite special challenges in the medical treatment of women with epilepsy, in particular preclinical animal studies were focused on males for decades and females have only recently moved into the focus of scientific interest. The intrahippocampal kainic acid (IHKA) mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is one of the most studied models in males reproducing electroencephalographic (EEG) and histopathological features of human TLE. Hippocampal paroxysmal discharges (HPDs) were described as drug resistant focal seizures in males. Here, we investigated the IHKA model in female mice, in particular drug-resistance of HPDs and the influence of antiseizure medications (ASMs) on the power spectrum. After injecting kainic acid (KA) unilaterally into the hippocampus of female mice, we monitored the development of epileptiform activity by local field potential (LFP) recordings. Subsequently, we evaluated the effect of the commonly prescribed ASMs lamotrigine (LTG), oxcarbazepine (OXC) and levetiracetam (LEV), as well as the benzodiazepine diazepam (DZP) with a focus on HPDs and power spectral analysis and assessed neuropathological alterations of the hippocampus. In the IHKA model, female mice replicated key features of human TLE as previously described in males. Importantly, HPDs in female mice did not respond to commonly prescribed ASMs in line with the drug-resistance in males, thus representing a suitable model of drug-resistant seizures. Intriguingly, we observed an increased occurrence of generalized seizures after LTG. Power spectral analysis revealed a pronounced increase in the delta frequency range after the higher dose of 30 mg/kg LTG. DZP abolished HPDs and caused a marked reduction over a wide frequency range (delta, theta, and alpha) of the power spectrum. By characterizing the IHKA model of TLE in female mice we address an important gap in basic research. Considering the special challenges complicating the therapeutic management of epilepsy in women, inclusion of females in preclinical studies is imperative. A well-characterized female model is a prerequisite for the development of novel therapeutic strategies tailored to sex-specific needs and for studies on the effect of epilepsy and ASMs during pregnancy.
Keywords: Drug-resistant seizures; Hippocampal paroxysmal discharges; Lamotrigine; Levetiracetam; Oxcarbazepine; Temporal lobe epilepsy.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest C. Schwarzer is co-founder of EpiBlok Therapeutics GmbH. None of the other authors has any conflict of interest to disclose. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Robust chronic convulsive seizures, high frequency oscillations, and human seizure onset patterns in an intrahippocampal kainic acid model in mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2022 May;166:105637. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105637. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 35091040 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Focal Seizures in the Intrahippocampal Kainate Mouse Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 Jun;22(6):497-506. doi: 10.1111/cns.12523. Epub 2016 Feb 22. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016. PMID: 26899987 Free PMC article.
-
Pronounced antiseizure activity of the subtype-selective GABAA positive allosteric modulator darigabat in a mouse model of drug-resistant focal epilepsy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Nov;28(11):1875-1882. doi: 10.1111/cns.13927. Epub 2022 Aug 14. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35965432 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of classic and novel anti-seizure medication in a kainate-induced model of chronic epilepsy.Epilepsy Res. 2023 Mar;191:107095. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2023.107095. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Epilepsy Res. 2023. PMID: 36812803
-
Long-term chemogenetic suppression of spontaneous seizures in a mouse model for temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2019 Nov;60(11):2314-2324. doi: 10.1111/epi.16368. Epub 2019 Oct 13. Epilepsia. 2019. PMID: 31608439
Cited by
-
Subthreshold Cannabidiol Potentiates Levetiracetam in the Kainic Acid Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: A Pilot Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;17(9):1187. doi: 10.3390/ph17091187. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338349 Free PMC article.
-
The Promise and Practicality of Addressing Sex as a Biological Variable and the Ovarian Cycle in Preclinical Epilepsy Research.Epilepsy Curr. 2024 Jul 25;24(4):274-279. doi: 10.1177/15357597241261463. eCollection 2024 Jul-Aug. Epilepsy Curr. 2024. PMID: 39309055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouilleret V, Ridoux V, Depaulis A, Marescaux C, Nehlig A, le Gal La Salle G. Recurrent seizures and hippocampal sclerosis following intrahippocampal kainate injection in adult mice: electroencephalography, histopathology and synaptic reorganization similar to mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1999;89:717–729. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4522(98)00401-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

