Cellular heterogeneity in TNF/TNFR1 signalling: live cell imaging of cell fate decisions in single cells
- PMID: 38467621
- PMCID: PMC10928192
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06559-z
Cellular heterogeneity in TNF/TNFR1 signalling: live cell imaging of cell fate decisions in single cells
Abstract
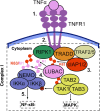
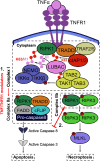
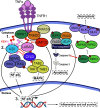
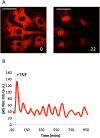
Cellular responses to TNF are inherently heterogeneous within an isogenic cell population and across different cell types. TNF promotes cell survival by activating pro-inflammatory NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathways but may also trigger apoptosis and necroptosis. Following TNF stimulation, the fate of individual cells is governed by the balance of pro-survival and pro-apoptotic signalling pathways. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms driving heterogenous responses to TNF, quantifying TNF/TNFR1 signalling at the single-cell level is crucial. Fluorescence live-cell imaging techniques offer real-time, dynamic insights into molecular processes in single cells, allowing for detection of rapid and transient changes, as well as identification of subpopulations, that are likely to be missed with traditional endpoint assays. Whilst fluorescence live-cell imaging has been employed extensively to investigate TNF-induced inflammation and TNF-induced cell death, it has been underutilised in studying the role of TNF/TNFR1 signalling pathway crosstalk in guiding cell-fate decisions in single cells. Here, we outline the various opportunities for pathway crosstalk during TNF/TNFR1 signalling and how these interactions may govern heterogenous responses to TNF. We also advocate for the use of live-cell imaging techniques to elucidate the molecular processes driving cell-to-cell variability in single cells. Understanding and overcoming cellular heterogeneity in response to TNF and modulators of the TNF/TNFR1 signalling pathway could lead to the development of targeted therapies for various diseases associated with aberrant TNF/TNFR1 signalling, such as rheumatoid arthritis, metabolic syndrome, and cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

