Generalizable disease detection using model ensemble on chest X-ray images
- PMID: 38467705
- PMCID: PMC10928229
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-56171-6
Generalizable disease detection using model ensemble on chest X-ray images
Abstract
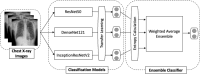
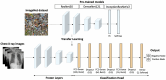
In the realm of healthcare, the demand for swift and precise diagnostic tools has been steadily increasing. This study delves into a comprehensive performance analysis of three pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures: ResNet50, DenseNet121, and Inception-ResNet-v2. To ensure the broad applicability of our approach, we curated a large-scale dataset comprising a diverse collection of chest X-ray images, that included both positive and negative cases of COVID-19. The models' performance was evaluated using separate datasets for internal validation (from the same source as the training images) and external validation (from different sources). Our examination uncovered a significant drop in network efficacy, registering a 10.66% reduction for ResNet50, a 36.33% decline for DenseNet121, and a 19.55% decrease for Inception-ResNet-v2 in terms of accuracy. Best results were obtained with DenseNet121 achieving the highest accuracy at 96.71% in internal validation and Inception-ResNet-v2 attaining 76.70% accuracy in external validation. Furthermore, we introduced a model ensemble approach aimed at improving network performance when making inferences on images from diverse sources beyond their training data. The proposed method uses uncertainty-based weighting by calculating the entropy in order to assign appropriate weights to the outputs of each network. Our results showcase the effectiveness of the ensemble method in enhancing accuracy up to 97.38% for internal validation and 81.18% for external validation, while maintaining a balanced ability to detect both positive and negative cases.
Keywords: Domain adaptation; Ensemble classifier; Pre-trained models; Transfer learning; X-ray imaging.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Douglas, L. J. Automated detection of COVID-19 with X-ray images by neural network based algorithms (2021).
-
- DeGrave AJ, Janizek JD, Lee S-I. Ai for radiographic covid-19 detection selects shortcuts over signal. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021;3:610–619. doi: 10.1038/s42256-021-00338-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical