Association between glycemic variability and short-term mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study of the MIMIC-IV database
- PMID: 38467770
- PMCID: PMC10928232
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-56564-7
Association between glycemic variability and short-term mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study of the MIMIC-IV database
Abstract
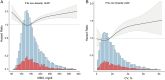
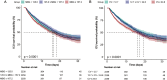
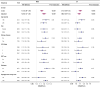
Acute kidney injury (AKI) represents a significant challenge to global public health problem and is associated with poor outcomes. There is still considerable debate about the effect of mean blood glucose (MBG) and coefficient of variation (CV) of blood glucose on the short-term mortality of AKI patients. This retrospective cohort study aimed to explore the association between glycemic variability and short-term mortality in patients with AKI. Data from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV) database were analyzed, including 6,777 adult AKI patients. MBG and CV on the first day of ICU admission were calculated to represent the overall glycemic status and variability during the ICU stay in AKI patients. The primary outcome indicator was ICU 30-day mortality of AKI patients. Multivariate Cox regression analysis and smoothed curve fitting were used to assess the relationship between blood glucose levels and mortality. Eventually, the ICU 30-day mortality rate of AKI patients was 23.5%. The increased MBG and CV were significantly correlated with ICU 30-day mortality (hazards ratio (HR) = 1.20, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.14-1.27; HR = 1.08, 95% CI 1.03-1.13). The smoothed curve fitting showed a U-shaped relationship between MBG on the first day of ICU admission and ICU 30-day mortality (inflection point = 111.3 mg/dl), while CV had a linear relationship with 30-day ICU mortality. Thus, we conclude that MBG and CV were significantly associated with short-term mortality in intensive care patients with AKI. Tighter glycemic control may be an effective measure to improve the prognosis of patients with AKI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Acute kidney injury. Nature reviews. Disease primers7, 51 (2021). 10.1038/s41572-021-00291-0 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

