Enhancer-promoter interactions become more instructive in the transition from cell-fate specification to tissue differentiation
- PMID: 38467791
- PMCID: PMC11018526
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01678-x
Enhancer-promoter interactions become more instructive in the transition from cell-fate specification to tissue differentiation
Abstract
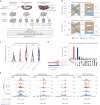
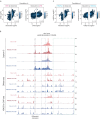
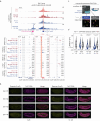
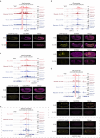
To regulate expression, enhancers must come in proximity to their target gene. However, the relationship between the timing of enhancer-promoter (E-P) proximity and activity remains unclear, with examples of uncoupled, anticorrelated and correlated interactions. To assess this, we selected 600 characterized enhancers or promoters with tissue-specific activity in Drosophila embryos and performed Capture-C in FACS-purified myogenic or neurogenic cells during specification and tissue differentiation. This enabled direct comparison between E-P proximity and activity transitioning from OFF-to-ON and ON-to-OFF states across developmental conditions. This showed remarkably similar E-P topologies between specified muscle and neuronal cells, which are uncoupled from activity. During tissue differentiation, many new distal interactions emerge where changes in E-P proximity reflect changes in activity. The mode of E-P regulation therefore appears to change as embryogenesis proceeds, from largely permissive topologies during cell-fate specification to more instructive regulation during terminal tissue differentiation, when E-P proximity is coupled to activation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- SPP 2202/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 787611 (DeCRyPT)/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 Ideas: European Research Council (FP7-IDEAS-ERC - Specific Programme & Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

