Inhibition of the AURKA/YAP1 axis is a promising therapeutic option for overcoming cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer stem cells
- PMID: 38467828
- PMCID: PMC11014903
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-024-02649-z
Inhibition of the AURKA/YAP1 axis is a promising therapeutic option for overcoming cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer stem cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: Inhibition of the AURKA/YAP1 axis is a promising therapeutic option for overcoming cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer stem cells.Br J Cancer. 2024 May;130(8):1414. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02667-x. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38575733 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Primary resistance to anti-EGFR therapies affects 40% of metastatic colorectal cancer patients harbouring wild-type RAS/RAF. YAP1 activation is associated with this resistance, prompting an investigation into AURKA's role in mediating YAP1 phosphorylation at Ser397, as observed in breast cancer.
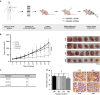
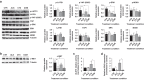
Methods: We used transcriptomic analysis along with in vitro and in vivo models of RAS/RAF wild-type CRC to study YAP1 Ser397 phosphorylation as a potential biomarker for cetuximab resistance. We assessed cetuximab efficacy using CCK8 proliferation assays and cell cycle analysis. Additionally, we examined the effects of AURKA inhibition with alisertib and created a dominant-negative YAP1 Ser397 mutant to assess its impact on cancer stem cell features.
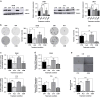
Results: The RAS/RAF wild-type CRC models exhibiting primary resistance to cetuximab prominently displayed elevated YAP1 phosphorylation at Ser397 primarily mediated by AURKA. AURKA-induced YAP1 phosphorylation was identified as a key trigger for cancer stem cell reprogramming. Consequently, we found that AURKA inhibition had the capacity to effectively restore cetuximab sensitivity and concurrently suppress the cancer stem cell phenotype.
Conclusions: AURKA inhibition holds promise as a therapeutic approach to overcome cetuximab resistance in RAS/RAF wild-type colorectal cancer, offering a potential means to counter the development of cancer stem cell phenotypes associated with cetuximab resistance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
RE: Reply to Rio-Vilariño and colleagues' article and misconception about YAP1 Ser 397 phosphorylation function.Br J Cancer. 2024 Jun;130(12):1892. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02720-9. Epub 2024 May 21. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38773253 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pitts TM, Kulikowski GN, Tan AC, Murray BW, Arcaroli JJ, Tentler JJ, et al. Association of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype with responsiveness to the p21-activated kinase inhibitor, PF-3758309, in colon cancer models. Front Pharm. 2013;4:35. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

