AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
- PMID: 38467836
- PMCID: PMC10987651
- DOI: 10.1038/s44320-024-00019-8
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
Abstract
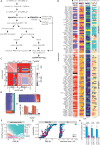
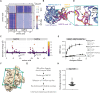
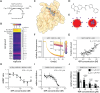
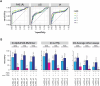
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) offer great opportunities to expand the druggable proteome and therapeutically tackle various diseases, but remain challenging targets for drug discovery. Here, we provide a comprehensive pipeline that combines experimental and computational tools to identify and validate PPI targets and perform early-stage drug discovery. We have developed a machine learning approach that prioritizes interactions by analyzing quantitative data from binary PPI assays or AlphaFold-Multimer predictions. Using the quantitative assay LuTHy together with our machine learning algorithm, we identified high-confidence interactions among SARS-CoV-2 proteins for which we predicted three-dimensional structures using AlphaFold-Multimer. We employed VirtualFlow to target the contact interface of the NSP10-NSP16 SARS-CoV-2 methyltransferase complex by ultra-large virtual drug screening. Thereby, we identified a compound that binds to NSP10 and inhibits its interaction with NSP16, while also disrupting the methyltransferase activity of the complex, and SARS-CoV-2 replication. Overall, this pipeline will help to prioritize PPI targets to accelerate the discovery of early-stage drug candidates targeting protein complexes and pathways.
Keywords: AlphaFold; Machine Learning; Protein–Protein Interactions; SARS-CoV-2; VirtualFlow.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. MV is an editorial advisory board member. This has no bearing on the editorial consideration of this article for publication.
Figures





Update of
-
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 14:2023.06.14.544560. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544560. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Apr;20(4):428-457. doi: 10.1038/s44320-024-00019-8. PMID: 37398436 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 14:2023.06.14.544560. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544560. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Apr;20(4):428-457. doi: 10.1038/s44320-024-00019-8. PMID: 37398436 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Discovery of a Druggable, Cryptic Pocket in SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 Using Allosteric Inhibitors.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 13;9(10):1918-1931. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00203. Epub 2023 Sep 20. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37728236 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insights into the 2'-O-methyltransferase of SARS-CoV-2.Virol Sin. 2024 Aug;39(4):619-631. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2024.07.001. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Virol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38969340 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the SARS-CoV-2-Host Protein-Protein Interactome by Affinity Purification Mass Spectrometry and Proximity-Dependent Biotin Labeling: A Rational and Straightforward Route to Discover Host-Directed Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 7;22(2):532. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020532. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the discovery of new chemotypes through ultra-large library docking.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2023 Mar;18(3):303-313. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2023.2171984. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 36714919 Review.
Cited by
-
Multimeric protein interaction and complex prediction: Structure, dynamics and function.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 May 16;27:1975-1997. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.009. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40496891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective disruption of DNMT1/ELK1 interactions induces DGKI re-expression and promotes temozolomide sensitivity of MGMTmethylated/DGKImethylated glioblastoma.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 Aug 30;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01943-8. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40886022 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic discovery of protein interaction interfaces using AlphaFold and experimental validation.Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Feb;20(2):75-97. doi: 10.1038/s44320-023-00005-6. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Mol Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 38225382 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress and future challenges in structure-based protein-protein interaction prediction.Mol Ther. 2025 May 7;33(5):2252-2268. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.04.003. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40195117 Review.
-
The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 8;29(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39516736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahdritz G, Bouatta N, Floristean C, Kadyan S, Xia Q, Gerecke W, O’Donnell TJ, Berenberg D, Fisk I, Zanichelli N et al (2022) OpenFold: retraining AlphaFold2 yields new insights into its learning mechanisms and capacity for generalization. Preprint at bioRxiv https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.20.517210v1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araujo MEG, de, Naschberger A, Fürnrohr BG, Stasyk T, Dunzendorfer-Matt T, Lechner S, Welti S, Kremser L, Shivalingaiah G, Offterdinger M, et al. Crystal structure of the human lysosomal mTORC1 scaffold complex and its impact on signaling. Science. 2017;358:377–381. doi: 10.1126/science.aao1583. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

