Lipidomics reveals new lipid-based lung adenocarcinoma early diagnosis model
- PMID: 38467839
- PMCID: PMC11018865
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-024-00052-y
Lipidomics reveals new lipid-based lung adenocarcinoma early diagnosis model
Abstract
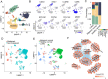
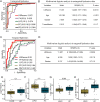
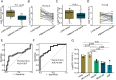
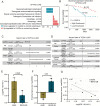
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) continues to pose a significant mortality risk with a lack of dependable biomarkers for early noninvasive cancer detection. Here, we find that aberrant lipid metabolism is significantly enriched in lung cancer cells. Further, we identified four signature lipids highly associated with LUAD and developed a lipid signature-based scoring model (LSRscore). Evaluation of LSRscore in a discovery cohort reveals a robust predictive capability for LUAD (AUC: 0.972), a result further validated in an independent cohort (AUC: 0.92). We highlight one lipid signature biomarker, PE(18:0/18:1), consistently exhibiting altered levels both in cancer tissue and in plasma of LUAD patients, demonstrating significant predictive power for early-stage LUAD. Transcriptome analysis reveals an association between increased PE(18:0/18:1) levels and dysregulated glycerophospholipid metabolism, which consistently displays strong prognostic value across two LUAD cohorts. The combined utility of LSRscore and PE(18:0/18:1) holds promise for early-stage diagnosis and prognosis of LUAD.
Keywords: Cancer Early Diagnosis Model; LSRscore; LUAD; Lipid Metabolism; Lipidomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bischoff P, Trinks A, Obermayer B, Pett JP, Wiederspahn J, Uhlitz F, Liang X, Lehmann A, Jurmeister P, Elsner A, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals distinct tumor microenvironmental patterns in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2021;40:6748–6758. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02054-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZLRK202333/Beijing hospital Authority Clinical Medicine Development Special Funding Support
- J.Z./Fundamental Research Funds for the General Universities
- 82202336/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021A1515110619/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- PKU2023LCXQ001/Clinical Medicine Plus X-Young Scholars Project of Peking Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

