The multiple roles of autophagy in uveal melanoma and the microenvironment
- PMID: 38467935
- PMCID: PMC10927889
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05576-3
The multiple roles of autophagy in uveal melanoma and the microenvironment
Abstract
Purpose: Uveal melanoma (UM) is the most common primary malignant intraocular tumor in adults, and effective clinical treatment strategies are still lacking. Autophagy is a lysosome-dependent degradation system that can encapsulate abnormal proteins, damaged organelles. However, dysfunctional autophagy has multiple types and plays a complex role in tumorigenicity depending on many factors, such as tumor stage, microenvironment, signaling pathway activation, and application of autophagic drugs.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature was conducted to analyze the role of autophagy in UM, as well as describing the development of autophagic drugs and the link between autophagy and the tumor microenvironment.
Results: In this review, we summarize current research advances regarding the types of autophagy, the mechanisms of autophagy, the application of autophagy inhibitors or agonists, autophagy and the tumor microenvironment. Finally, we also discuss the relationship between autophagy and UM.
Conclusion: Understanding the molecular mechanisms of how autophagy differentially affects tumor progression may help to design better therapeutic regimens to prevent and treat UM.
Keywords: Autophagy; Drug target; Microenvironment; Uveal melanoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
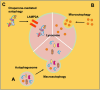
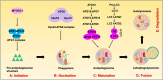
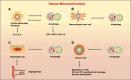
References
-
- Aita VM et al (1999) Cloning and genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17q21. Genomics 59:59–65 - PubMed
-
- Ajoolabady A, Aghanejad A, Bi Y, Zhang Y, Aslkhodapasandhukmabad H, Abhari A, Ren J (2020) Enzyme-based autophagy in anti-neoplastic management: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1874:188366. 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188366 - PubMed
-
- Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC, Debnath J (2019) Targeting autophagy in cancer: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Discov 9:1167–1181. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0292 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini G, Musi E, Ho AL, de Stanchina E, Schwartz GK (2013) Inhibition of mutant GNAQ signaling in uveal melanoma induces AMPK-dependent autophagic cell death. Mol Cancer Ther 12:768–776. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

