Group XIV C-type lectins: emerging targets in tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 38468017
- PMCID: PMC11021320
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-024-09907-x
Group XIV C-type lectins: emerging targets in tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
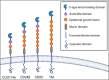
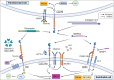
C-type lectins, distinguished by a C-type lectin binding domain (CTLD), are an evolutionarily conserved superfamily of glycoproteins that are implicated in a broad range of physiologic processes. The group XIV subfamily of CTLDs are comprised of CD93, CD248/endosialin, CLEC14a, and thrombomodulin/CD141, and have important roles in creating and maintaining blood vessels, organizing extracellular matrix, and balancing pro- and anti-coagulative processes. As such, dysregulation in the expression and downstream signaling pathways of these proteins often lead to clinically relevant pathology. Recently, group XIV CTLDs have been shown to play significant roles in cancer progression, namely tumor angiogenesis and metastatic dissemination. Interest in therapeutically targeting tumor vasculature is increasing and the search for novel angiogenic targets is ongoing. Group XIV CTLDs have emerged as key moderators of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis, thus offering substantial therapeutic promise for the clinic. Herein, we review our current knowledge of group XIV CTLDs, discuss each's role in malignancy and associated potential therapeutic avenues, briefly discuss group XIV CTLDs in the context of two other relevant lectin families, and offer future direction in further elucidating mechanisms by which these proteins function and facilitate tumor growth.
Keywords: C-type lectin; Immunotherapy; Tumor angiogenesis; Vessel normalization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.S., R.D.S., and Y. Z. have a patent filed related to the CD93 research project. Y.Z. consults for Dynamicure Biotechnology. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multimerin-2 is a ligand for group 14 family C-type lectins CLEC14A, CD93 and CD248 spanning the endothelial pericyte interface.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 2;36(44):6097-6108. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.214. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28671670 Free PMC article.
-
C-type lectin domain group 14 proteins in vascular biology, cancer and inflammation.FEBS J. 2019 Sep;286(17):3299-3332. doi: 10.1111/febs.14985. Epub 2019 Jul 29. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 31287944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-type lectin family XIV members and angiogenesis.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):3954-3962. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10760. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31579078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel monoclonal antibodies specific for CTLD-SSC and sialomucin domains of endosialin, a mural cell marker of tumor vasculature.Int J Oncol. 2012 Oct;41(4):1365-72. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1566. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22824847
-
Human antibodies targeting the C-type lectin-like domain of the tumor endothelial cell marker clec14a regulate angiogenic properties in vitro.Oncogene. 2013 Nov 28;32(48):5449-57. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.156. Epub 2013 May 6. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23644659 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Modulation of blood-tumor barrier transcriptional programs improves intratumoral drug delivery and potentiates chemotherapy in GBM.Sci Adv. 2025 Feb 28;11(9):eadr1481. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr1481. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40009687 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

