Effects of intratesticular injection of hypertonic mannitol and saline on the quality of donkey sperm, indicators of oxidative stress and testicular tissue pathology
- PMID: 38468237
- PMCID: PMC10926677
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-03915-1
Effects of intratesticular injection of hypertonic mannitol and saline on the quality of donkey sperm, indicators of oxidative stress and testicular tissue pathology
Abstract
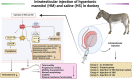
Objectives: The aim of the present study was to examine donkey sperm quality after intratesticular injection of hypertonic mannitol (HM) and saline (HS).
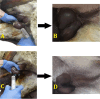
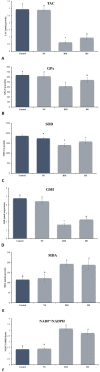
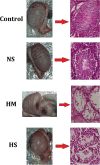
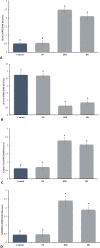
Methods: Randomly assigned to five treatment groups were 15 adult male donkeys: (1) Control group (no treatment), (2) Surgery group (surgical castration for testosterone control), (3) NS group (normal saline intratesticular injection), (4) HS group (hypertonic saline), and (5) HM group. We injected 20 mL per testicle. We took 5 mL blood from all donkeys before injection. Castration was performed under general anesthesia 60 days later. Samples included blood and testicular tissue. Total motility (TM), progressive motility (PM), movementy features, DNA damage, morphology, viability, and plasma membrane functionality were evaluated. Hormone analyses, histomorphometric studies and oxidative stress indices including total antioxidant capacity (TAC), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and NADP+/NADPH were evaluated. Apoptosis, pyroptosis-related Bax, Caspase-1, GSDMD, and Bcl-2 expression were also assessed.
Results: In HS and HM groups, testosterone, epididymal sperm count, motility, viability, and plasma membrane functionality dropped while sperm DNA damage increased. HS and HM groups had significantly lower histomorphometric parameters, TAC, GPx, SOD, GSH, and Bcl-2 gene expression. MDA, NADP+/NADPH, Bax, Caspase-1, and GSDMD gene expression were substantially higher in the HS and HM groups than in the control group.
Conclusions: Toxic effects of hypertonic saline and mannitol on reproductive parameters were seen following, hence, they might be considered as a good chemical sterilizing treatment in donkeys.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Chemical sterilization; Donkey; Genes expression; Pyroptosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allicin and hesperidin protect sperm production from environmental toxins in mice.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 24;15(1):14224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97730-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40274915 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of quercetin and mirtazapine on spermatogenesis and testis structure in phenylhydrazine-induced hemolytic anemia mice: An experimental study.Food Chem Toxicol. 2024 Jul;189:114732. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2024.114732. Epub 2024 May 11. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38740240
-
Synergistic protective effects of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol and hydroxytyrosol in male rats against induced heat stress-induced reproduction damage.Food Chem Toxicol. 2024 Aug;190:114818. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2024.114818. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38880467
-
Sterilization of male stray dogs with a single intratesticular injection of calcium chloride: a dose-dependent study.Contraception. 2007 May;75(5):390-400. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2007.01.022. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Contraception. 2007. PMID: 17434022
-
Taurine effects on Bisphenol A-induced oxidative stress in the mouse testicular mitochondria and sperm motility.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2020 Oct 6;24(4):428-435. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20200017. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32550655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Male animal sterilization: history, current practices, and potential methods for replacing castration.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 3;11:1409386. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1409386. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39027909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Glucan and resveratrol mitigate lead induced reproductive toxicity in male mice.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 25;15(1):31277. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16510-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40855167 Free PMC article.
-
The synergistic activity of fisetin on quercetin improves testicular recover in ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 8;15(1):12053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96413-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40199993 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Inhibin Immunization on Reproductive Hormones and Testicular Morphology of Dezhou Donkeys During the Non-Breeding Season.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 13;15(6):813. doi: 10.3390/ani15060813. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamed MA, Amin YA, Mohamed RH, El-Adl M, Bazeed SM, Elnegiry AA, et al. Evaluation of chemical castration using intra-testicular injection of zinc gluconate into the testis of the male donkey versus surgical castration: antimullerian hormone as an endpoint marker. BMC Vet Res. 2023;19:140. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03694-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Okwee-Acai J, Ojok L, Acon J. Testicular morphologic and hormonal responses to an intratesticular injection of lactic acid for induction of chemosterilisation in adult mubende goats. Afr J Anim Biomed Sci. 2008;3:5–11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

