Underlying mechanisms and cardioprotective effects of SGLT2i and GLP-1Ra: insights from cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- PMID: 38468245
- PMCID: PMC10926589
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02181-7
Underlying mechanisms and cardioprotective effects of SGLT2i and GLP-1Ra: insights from cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Abstract
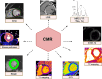
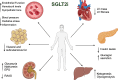
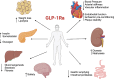
Originally designed as anti-hyperglycemic drugs, Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1Ra) and Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have demonstrated protective cardiovascular effects, with significant impact on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Despite several mechanisms have been proposed, the exact pathophysiology behind these effects is not yet fully understood. Cardiovascular imaging is key for the evaluation of diabetic patients, with an established role from the identification of early subclinical changes to long-term follow up and prognostic assessment. Among the different imaging modalities, CMR may have a key-role being the gold standard for volumes and function assessment and having the unique ability to provide tissue characterization. Novel techniques are also implementing the possibility to evaluate cardiac metabolism through CMR and thereby further increasing the potential role of the modality in this context. Aim of this paper is to provide a comprehensive review of changes in CMR parameters and novel CMR techniques applied in both pre-clinical and clinical studies evaluating the effects of SGLT2i and GLP-1Ra, and their potential role in better understanding the underlying CV mechanisms of these drugs.
Keywords: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance; Diabetic cardiomyopathy; GLP-1Ra; SGLT2i.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. novembre. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Di Cesare M, Bentham J, Stevens GA, Zhou B, Danaei G, Lu Y et al. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387(10026):1377–1396. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X. Erratum in: Lancet. 2016;387(10032):1998. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Coady S, Sorlie PD, D’Agostino RB, Pencina MJ, Vasan RS et al. Increasing Cardiovascular Disease Burden Due to Diabetes Mellitus: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 27 marzo. 2007;115(12):1544–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PNRR-National Center for Gene Therapy and Drugs based on RNA Technology (CN00000041)/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PRIN 2020L45ZWA_005/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PNRR-National Center for Gene Therapy and Drugs based on RNA Technology (CN00000041)/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PSC SALUTE 2014-2020 - POS4 "Cal-Hub-Ria" (T4-AN-09)/Ministero della Salute
- PSC SALUTE 2014-2020 - POS4 "Cal-Hub-Ria" (T4-AN-09)/Ministero della Salute
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

