The influence of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cognitive function in individuals without dementia: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis
- PMID: 38468309
- PMCID: PMC10929146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03296-0
The influence of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cognitive function in individuals without dementia: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) have been suggested as a cognitive enhancing agent, though their effect is doubtful. We aimed to examine the effect of n-3 PUFA on the cognitive function of middle-aged or older adults without dementia.
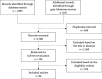
Methods: We reviewed randomized controlled trials of individuals aged 40 years or older. We systematically searched PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Cochrane Library databases. We used the restricted cubic splines model for non-linear dose-response meta-analysis in terms of the standardized mean difference with 95% confidence intervals.
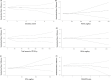
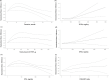
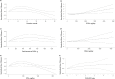
Results: The current meta-analysis on 24 studies (n 9660; follow-up 3 to 36 months) found that the beneficial effect on executive function demonstrates an upward trend within the initial 12 months of intervention. This effect is prominently observed with a daily intake surpassing 500 mg of n-3 PUFA and up to 420 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Furthermore, these trends exhibit heightened significance in regions where the levels of blood docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) + EPA are not very low.
Conclusions: Supplementation of n-3 PUFA may confer potential benefits to executive function among the middle-aged and elderly demographic, particularly in individuals whose dietary DHA + EPA level is not substantially diminished.
Keywords: Cognitive function; Dose–response meta-analysis; Mild cognitive impairment; N-3 PUFA; Omega-3; Polyunsaturated fatty acids.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

