Needle artifact reduction during interventional CT procedures using a silver filter
- PMID: 38468322
- PMCID: PMC10926571
- DOI: 10.1186/s42490-024-00076-y
Needle artifact reduction during interventional CT procedures using a silver filter
Abstract
Background: MAR algorithms have not been productized in interventional imaging because they are too time-consuming. Application of a beam hardening filter can mitigate metal artifacts and doesn't increase computational burden. We evaluate the ability to reduce metal artifacts of a 0.5 mm silver (Ag) additional filter in a Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT) scanner during CT-guided biopsy procedures.
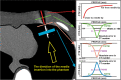
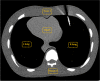
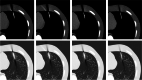
Methods: A biopsy needle was positioned inside the lung field of an anthropomorphic phantom (Lungman, Kyoto Kagaku, Kyoto, Japan). CT acquisitions were performed with beam energies of 100 kV, 120 kV, 135 kV, and 120 kV with the Ag filter and reconstructed using a filtered back projection algorithm. For each measurement, the CTDIvol was kept constant at 1 mGy. Quantitative profiles placed in three regions of the artifact (needle, needle tip, and trajectory artifacts) were used to obtain metrics (FWHM, FWTM, width at - 100 HU, and absolute error in HU) to evaluate the blooming artifact, artifact width, change in CT number, and artifact range. An image quality analysis was carried out through image noise measurement. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used to find significant differences between the conventional CT beam energies and the Ag filtered 120 kV beam.
Results: The 120 kV-Ag is shown to have the shortest range of artifacts compared to the other beam energies. For needle tip and trajectory artifacts, a significant reduction of - 53.6% (p < 0.001) and - 48.7% (p < 0.001) in the drop of the CT number was found, respectively, in comparison with the reference beam of 120 kV as well as a significant decrease of up to - 34.7% in the artifact width (width at - 100 HU, p < 0.001). Also, a significant reduction in the blooming artifact of - 14.2% (FWHM, p < 0.001) and - 53.3% (FWTM, p < 0.001) was found in the needle artifact. No significant changes (p > 0.05) in image noise between the conventional energies and the 120 kV-Ag were found.
Conclusions: A 0.5 mm Ag additional MDCT filter demonstrated consistent metal artifact reduction generated by the biopsy needle. This reduction may lead to a better depiction of the target and surrounding structures while maintaining image quality.
Keywords: CT artifact; CT filter; Interventional CT.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TPS receives research support from Canon Medical Systems USA and GE Healthcare; consultant with AiDoc, ALARA Imaging, AstoCT/LeoCancerCare; medical advisory board of Imalogix; founded RadUnity. MGW is consultant for HistoSonics Inc; sponsored research agreement with Siemens Healthineers and Canon Medical System USA. FTL is consultant with Ethicon, Inc.; Patents, Royalties with Medtronic, Inc.; Board of Directors of Shareholder; Stockholder, Elucent Medical, Inc; Medical Advisory Board of Canon Medical Systems. CARM, BH, and JT declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Technical Note: Evaluation of a 160-mm/256-row CT scanner for whole-heart quantitative myocardial perfusion imaging.Med Phys. 2016 Aug;43(8):4821. doi: 10.1118/1.4957389. Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27487900
-
Metal artifact correction in photon-counting detector computed tomography: metal trace replacement using high-energy data.Med Phys. 2023 Jan;50(1):380-396. doi: 10.1002/mp.16049. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36227611
-
Reduction of guide needle streak artifact in CT-guided biopsy.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Dec;25(12):1929-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.08.028. Epub 2014 Oct 11. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25311968
-
Generation of hybrid sinograms for the recovery of kV-CT images with metal artifacts for helical tomotherapy.Med Phys. 2015 Aug;42(8):4654-67. doi: 10.1118/1.4926552. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26233193
-
Combined application of virtual monoenergetic high keV images and the orthopedic metal artifact reduction algorithm (O-MAR): effect on image quality.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019 Feb;44(2):756-765. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1748-0. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019. PMID: 30135970
References
-
- Szczykutowicz TP. The CT handbook: optimizing protocols for today's feature-rich scanners. Medical Physics Publishing; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
