Oxymatrine protects articular chondrocytes from IL-1β-induced damage through autophagy activation via AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibition
- PMID: 38468339
- PMCID: PMC10926585
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-04667-2
Oxymatrine protects articular chondrocytes from IL-1β-induced damage through autophagy activation via AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibition
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease characterized by persistent articular cartilage degeneration and synovitis. Oxymatrine (OMT) is a quinzolazine alkaloid extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine, matrine, and possesses anti-inflammatory properties that may help regulate the pathogenesis of OA; however, its mechanism has not been elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the effects of OMT on interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced damage and the potential mechanisms of action.
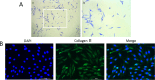
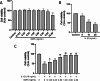
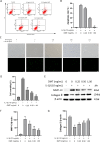
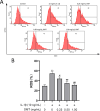
Methods: Chondrocytes were isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats. Toluidine blue and Collagen II immunofluorescence staining were used to determine the purity of the chondrocytes. Thereafter, the chondrocytes were subjected to IL-1β stimulation, both in the presence and absence of OMT, or the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA). Cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay and SYTOX Green staining. Additionally, flow cytometry was used to determine cell apoptosis rate and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. The protein levels of AKT, mTOR, LC3, P62, matrix metalloproteinase-13, and collagen II were quantitatively analyzed using western blotting. Immunofluorescence was used to assess LC3 expression.
Results: OMT alleviated IL-1β-induced damage in chondrocytes, by increasing the survival rate, reducing the apoptosis rates of chondrocytes, and preventing the degradation of the cartilage matrix. In addition, OMT decreased the ROS levels and inhibited the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway while promoting autophagy in IL-1β treated chondrocytes. However, the effectiveness of OMT in improving chondrocyte viability under IL-1β treatment was limited when autophagy was inhibited by 3-MA.
Conclusions: OMT decreases oxidative stress and inhibits the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to enhance autophagy, thus inhibiting IL-1β-induced damage. Therefore, OMT may be a novel and effective therapeutic agent for the clinical treatment of OA.
Keywords: AKT/mTOR pathway; Autophagy; Chondrocytes; Oxymatrine; interleukin-1β.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 May;89:1252-1261. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.130. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28320092
-
Oroxin B alleviates osteoarthritis through anti-inflammation and inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancement of autophagy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 1;13:1060721. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1060721. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36531454 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the mechanism of IL-1β-Mediated Piezo1 expression regulation of chondrocyte autophagy and apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling Pathway.Tissue Cell. 2024 Feb;86:102291. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102291. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Tissue Cell. 2024. PMID: 38134572
-
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020 Apr;28(4):400-409. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.02.027. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 32081707 Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species, aging and articular cartilage homeostasis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Feb 20;132:73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.038. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30176344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxymatrine attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via APE1‑mediated regulation of the PINK1/Parkin pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Oct;32(4):262. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13627. Epub 2025 Jul 25. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40709402 Free PMC article.
-
Recent development of mitochondrial metabolism and dysfunction in osteoarthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 13;16:1538662. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1538662. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40017603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of granulosa cells in dairy cow follicular cysts by activating autophagy via the SIRT1/ROS/AMPK signaling pathway.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 5;15(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01078-5. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39232832 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

