A qualitative study about critical appraisal of medical literature learning among medical students
- PMID: 38468586
- PMCID: PMC11261492
A qualitative study about critical appraisal of medical literature learning among medical students
Abstract
Introduction: Skills in critical appraisal of medical literature are compulsory to achieve in medical practice. This step is the third step of the evidence-based medicine process whose main role is to bridge a gap between scientific evidence and practice. Acquiring skills in critical appraisal of the literature has been reported to be challenging for the trainees with different limits according to their levels, backgrounds or specialties.
Aim: To assess the limits and factors influencing the practice of appraising literature of different students from the same faculty. This faculty included training of biostatistics and preventive medicine in the curriculum during the first 2 years of medical education without linking this learning to the evidence-based medicine practice.
Methods: The authors performed a qualitative study including volunteers who attended voluntarily the same training about critical appraisal of medical literature. The study was based on a satisfaction questionnaire fulfilled by all the participants at the end of the training and on an individual semi-structured interviews programmed 3 months after the training. The satisfaction questionnaire was rated by the authors. The authors proceeded also to a content analysis of the interviews following 3 steps: pre-analysis, treatment of the results, and interpretation.
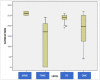
Results: All the participants (95) fulfilled the questionnaire. The satisfaction's mean score revealed a general moderate satisfaction. Eleven students agreed to be interviewed: Five students from the third year of medical education, 2 students from the second year of medical education, 2 postgraduate students and 2 family doctors. The main themes discussed by the interviewees consisted of training organization, the assessment, the impact on research and the impact on the care process.
Conclusion: To promote EBM learning, medical students first need to actively participate to interactive learning, introduced early and gradually into the curriculum and integrating all specialties including postgraduate students.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A qualitative study of factors promoting EBM learning among medical students in Japan.Int J Med Educ. 2022 Aug 26;13:215-220. doi: 10.5116/ijme.62eb.7c19. Int J Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 36036207 Free PMC article.
-
Is critical thinking potential correlated to critical appraisal skills of medical literature?Tunis Med. 2023 Jul 5;101(7):602-608. Tunis Med. 2023. PMID: 38445420 Free PMC article. English.
-
Formal evidence-based medicine instruction in Turkish undergraduate medical education: an initial evaluation.BMC Med Educ. 2021 Aug 19;21(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02876-5. BMC Med Educ. 2021. PMID: 34407804 Free PMC article.
-
Take-Home Training in Laparoscopy.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5335. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385174 Review.
-
Teaching Medical Students to Teach: A Narrative Review and Literature-Informed Recommendations for Student-as-Teacher Curricula.Acad Med. 2022 Jun 1;97(6):909-922. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004608. Epub 2022 May 19. Acad Med. 2022. PMID: 35108235 Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

