Machine Learning-Based Nomogram for Predicting Overall Survival in Elderly Patients with Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Ablation Therapy
- PMID: 38468611
- PMCID: PMC10926877
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S450825
Machine Learning-Based Nomogram for Predicting Overall Survival in Elderly Patients with Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Ablation Therapy
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of the study is to identify and evaluate multifaceted factors impacting the survival of elderly cirrhotic HCC patients following ablation therapy, with the goal of constructing a nomogram to predict their 3-, 5-, and 8-year overall survival (OS).
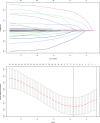
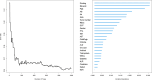
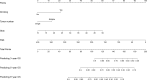
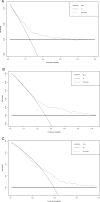
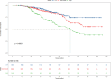
Patients and methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 736 elderly cirrhotic HCC patients who underwent ablation therapy between 2014 and 2022. LASSO regression, random survival forest (RSF), and multivariate Cox analyses were employed to identify independent prognostic factors for OS, followed by the development and validation of a predictive nomogram. Harrell's concordance index (C-index), calibration plot and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to assess the performance of the nomogram. The nomogram was finally utilized to stratify patients into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups, aiming to assess its efficacy in precisely discerning individuals with diverse overall survival outcomes.
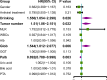
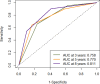
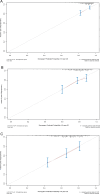
Results: Alcohol drinking, tumor number, globulin (Glob) and prealbumin (Palb) were identified and integrated to establish a novel prognostic nomogram. The nomogram exhibited strong discriminative ability with C-indices of 0.723 (training cohort) and 0.693 (validation cohort), along with significant Area Under the Curve (AUC) values for 3-year, 5-year, and 8-year OS in both cohorts (0.758, 0.770, and 0.811 for training cohort; 0.744, 0.699 and 0.737 for validation cohort). Calibration plots substantiated its consistency, while DCA curves corroborated its clinical utility. The nomogram further demonstrated exceptional effectiveness in discerning distinct risk populations, highlighting its robust applicability for prognostic stratification.
Conclusion: Our study successfully developed and validated a robust nomogram model based on four key clinical parameters for predicting 3-, 5- and 8-year OS among elderly cirrhotic HCC patients following ablation therapy. The nomogram exhibited a remarkable capability in identifying high-risk patients, furnishing clinicians with invaluable insights for postoperative surveillance and tailored therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: HCC; LASSO regression; OS; RSF; hepatocellular carcinoma; nomogram; overall survival; random survival forest.
© 2024 Qiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel nomogram to predict the overall survival of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients following ablation therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 7;14:1340286. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1340286. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38384805 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nomogram based on the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio for patients with compensated cirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma after local ablation.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 11;14:1406764. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1406764. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39055565 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of nomogram to predict overall survival and disease-free survival after surgical resection in elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 May 24;14:1395740. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1395740. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38854717 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and validation of a novel nomogram to predict overall survival after radical nephrectomy].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023 Aug 23;45(8):681-689. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20221027-00722. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37580273 Chinese.
-
Development and Validation of a Prognostic Model for Transarterial Chemoembolization in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Preoperative Serum Prealbumin.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Dec 13;10:2239-2250. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S433245. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 38107543 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and Validation of Machine Learning Models for Predicting 7-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Neurocrit Care. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1007/s12028-025-02308-y. Online ahead of print. Neurocrit Care. 2025. PMID: 40563047
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

