Evaluating the efficacy and safety of oral triple sequential combination therapy for treating patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A multicenter retrospective study
- PMID: 38468630
- PMCID: PMC10925724
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.12351
Evaluating the efficacy and safety of oral triple sequential combination therapy for treating patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A multicenter retrospective study
Abstract
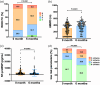
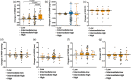
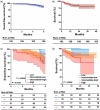
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of an oral sequential triple combination therapy with selexipag after dual combination therapy with endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5I)/riociguat in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients. A total of 192 PAH patients from 10 centers had received oral sequential selexipag therapy after being on dual-combination therapy with ERA and PDE5i/riociguat for a minimum of 3 months. Clinical data were collected at baseline and after 6 months of treatment. The study analyzed the event-free survival at 6 months and all-cause death over 2 years. At baseline, the distribution of patients among the risk groups was as follows: 22 in the low-risk group, 35 in the intermediate-low-risk group, 91 in the intermediate-high-risk group, and 44 in the high-risk group. After 6 months of treatment, the oral sequential triple combination therapy resulted in reduced NT-proBNP levels (media from 1604 to 678 pg/mL), a decline in the percentage of WHO-FC III/IV (from 79.2% to 60.4%), an increased in the 6MWD (from 325 ± 147 to 378 ± 143 m) and a rise in the percentage of patients with three low-risk criteria (from 5.7% to 13.5%). Among the low-risk group, there was an improvement in the right heart remodeling, marked by a decrease in right atrium area and eccentricity index. The intermediate-low-risk group exhibited significant enhancements in WHO-FC and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion. For those in the intermediate-high and high-risk groups, there were marked improvements in activity tolerance, as reflected by WHO-FC and 6MWD. The event-free survival rate at 6 months stood at 88%. Over the long-term follow-up, the survival rates at 1 and 2 years were 86.5% and 86.0%, respectively. In conclusion, the oral sequential triple combination therapy enhanced both exercise capacity and cardiac remodeling across PAH patients of different risk stratifications.
Keywords: event; oral sequential triple combination therapy; pulmonary arterial hypertension; risk stratification; survival.
© 2024 The Authors. Pulmonary Circulation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, Carlsen J, Coats AJS, Escribano‐Subias P, Ferrari P, Ferreira DS, Ghofrani HA, Giannakoulas G, Kiely DG, Mayer E, Meszaros G, Nagavci B, Olsson KM, Pepke‐Zaba J, Quint JK, Rådegran G, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Tonia T, Toshner M, Vachiery JL, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Delcroix M, Rosenkranz S, Schwerzmann M, Dinh‐Xuan AT, Bush A, Abdelhamid M, Aboyans V, Arbustini E, Asteggiano R, Barberà JA, Beghetti M, Čelutkienė J, Cikes M, Condliffe R, de Man F, Falk V, Fauchier L, Gaine S, Galié N, Gin‐Sing W, Granton J, Grünig E, Hassoun PM, Hellemons M, Jaarsma T, Kjellström B, Klok FA, Konradi A, Koskinas KC, Kotecha D, Lang I, Lewis BS, Linhart A, Lip GYH, Løchen ML, Mathioudakis AG, Mindham R, Moledina S, Naeije R, Nielsen JC, Olschewski H, Opitz I, Petersen SE, Prescott E, Rakisheva A, Reis A, Ristić AD, Roche N, Rodrigues R, Selton‐Suty C, Souza R, Swift AJ, Touyz RM, Ulrich S, Wilkins MR, Wort SJ. 2022 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(38):3618–3731. - PubMed
-
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Barst RJ, Badesch DB, Frost AE, McGoon MD. An evaluation of long‐term survival from time of diagnosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension from the REVEAL registry. Chest. 2012;142(2):448–456. - PubMed
-
- Gall H, Felix JF, Schneck FK, Milger K, Sommer N, Voswinckel R, Franco OH, Hofman A, Schermuly RT, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Ghofrani HA. The Giessen pulmonary hypertension registry: survival in pulmonary hypertension subgroups. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2017;36(9):957–967. - PubMed
-
- D'Alto M, Badagliacca R, Argiento P, Romeo E, Farro A, Papa S, Sarubbi B, Russo MG, Vizza CD, Golino P, Naeije R. Risk reduction and right heart reverse remodeling by upfront triple combination therapy in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest. 2020;157(2):376–383. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

