The interactions between ineffective erythropoiesis and ferroptosis in β-thalassemia
- PMID: 38468700
- PMCID: PMC10925657
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1346173
The interactions between ineffective erythropoiesis and ferroptosis in β-thalassemia
Abstract
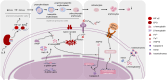
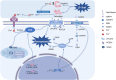
In Guangxi, Hainan, and Fujian Province in southern China, β-thalassemia is a frequent monogenic hereditary disorder that is primarily defined by hemolytic anemia brought on by inefficient erythropoiesis. It has been found that ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia is closely associated with a high accumulation of Reactive oxygen species, a product of oxidative stress, in erythroid cells. During recent years, ferroptosis is an iron-dependent lipid peroxidation that involves abnormalities in lipid and iron metabolism as well as reactive oxygen species homeostasis. It is a recently identified kind of programmed cell death. β-thalassemia patients experience increased iron release from reticuloendothelial cells and intestinal absorption of iron, ultimately resulting in iron overload. Additionally, the secretion of Hepcidin is inhibited in these patients. What counts is both ineffective erythropoiesis and ferroptosis in β-thalassemia are intricately linked to the iron metabolism and Reactive oxygen species homeostasis. Consequently, to shed further light on the pathophysiology of β-thalassemia and propose fresh ideas for its therapy, this paper reviews ferroptosis, ineffective erythropoiesis, and the way they interact.
Keywords: ROS; ferroptosis; ineffective erythropoiesis; iron overload; pathogenesis; β-thalassemia.
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Zheng, Chen, Xu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

