Modeling-informed Engineered Genetic Incompatibility strategies to overcome resistance in the invasive Drosophila suzukii
- PMID: 38468757
- PMCID: PMC10926386
- DOI: 10.3389/finsc.2022.1063789
Modeling-informed Engineered Genetic Incompatibility strategies to overcome resistance in the invasive Drosophila suzukii
Abstract
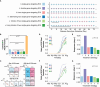
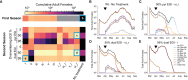
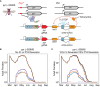
Engineered Genetic Incompatibility (EGI) is an engineered extreme underdominance genetic system wherein hybrid animals are not viable, functioning as a synthetic speciation event. There are several strategies in which EGI could be leveraged for genetic biocontrol of pest populations. We used an agent-based model of Drosophila suzukii (Spotted Wing Drosophila) to determine how EGI would fare with high rates of endemic genetic resistance alleles. We discovered a surprising failure mode wherein field-generated females convert an incompatible male release program into a population replacement gene drive. Local suppression could still be attained in two seasons by tailoring the release strategy to take advantage of this effect, or alternatively in one season by altering the genetic design of release agents. We show in this work that data from modeling can be utilized to recognize unexpected emergent phenomena and a priori inform genetic biocontrol treatment design to increase efficacy.
Keywords: agent-based modeling; genetic biocontrol; incompatible insect technique (IIT); resistance; spotted wing drosophila.
Copyright © 2022 Sychla, Feltman, Hutchison and Smanski.
Conflict of interest statement
MJS is a cofounder of Novoclade, Inc., and he and NRF holds patents related to the EGI technology. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Corrigendum: Modeling-informed Engineered Genetic Incompatibility strategies to overcome resistance in the invasive Drosophila suzukii.Front Insect Sci. 2024 Jan 12;3:1360167. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2023.1360167. eCollection 2023. Front Insect Sci. 2024. PMID: 38469520 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-based split homing gene drive targeting doublesex for population suppression of the global fruit pest Drosophila suzukii.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 20;120(25):e2301525120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2301525120. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37307469 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting thresholds for population replacement gene drives.BMC Biol. 2024 Feb 19;22(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01823-2. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 38369493 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Chemical Ecology of the Spotted Wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii) and its Applications.J Chem Ecol. 2018 Oct;44(10):922-939. doi: 10.1007/s10886-018-1000-y. Epub 2018 Jul 27. J Chem Ecol. 2018. PMID: 30054769 Review.
-
Optimization of native biocontrol agents, with parasitoids of the invasive pest Drosophila suzukii as an example.Evol Appl. 2018 Jun 14;11(9):1473-1497. doi: 10.1111/eva.12648. eCollection 2018 Oct. Evol Appl. 2018. PMID: 30344621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

