Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Conventional and Organic Insecticides on the Parasitoid Trissolcus japonicus, a Biological Control Agent for Halyomorpha halys
- PMID: 38468889
- PMCID: PMC10926492
- DOI: 10.3389/finsc.2021.685755
Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Conventional and Organic Insecticides on the Parasitoid Trissolcus japonicus, a Biological Control Agent for Halyomorpha halys
Abstract
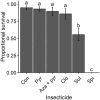
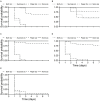
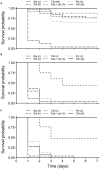
The egg parasitoid Trissolcus japonicus is a natural enemy of Halyomorpha halys, a polyphagous invasive pest in Europe and North and South America. Integration of chemical and biological control tactics could facilitate effective and sustainable integrated pest management programs. This study was conducted to assess (i) the lethal effects of field rates, (ii) the sublethal effects of maximum and half field rates, and (iii) the lethal effects of different routes of exposure of three organic and two conventional insecticides against T. japonicus. Maximum field rates of spinosad and sulfoxaflor resulted in acute lethal toxicity to adult T. japonicus 1 week after residual contact exposure. Maximum and half field rates of pyrethrins, the mixture of azadirachtin and pyrethrins, and clothianidin caused sublethal effects to female wasps through residual contact exposure. Furthermore, all insecticides caused acute lethal effects 1 week after ingestion by unmated female wasps. Taken together, these results suggest that careful planning is necessary to ensure compatibility between biological and chemical control for H. halys. The insecticides evaluated in this study varied in toxicity to T. japonicus and should be used with caution to conserve this natural enemy for biological control of H. halys.
Keywords: brown marmorated stink bug; exposure routes; fecundity; fertility; longevity; samurai wasp; sex.
Copyright © 2021 Ribeiro, Holle, Hutchison and Koch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sensitivity of the Egg Parasitoid Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) to Field and Laboratory-Applied Insecticide Residue.J Econ Entomol. 2019 Sep 23;112(5):2077-2084. doi: 10.1093/jee/toz127. J Econ Entomol. 2019. PMID: 31115460
-
Surveys in northern Utah for egg parasitoids of Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) detect Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae).Biodivers Data J. 2020 Aug 13;8:e53363. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.8.e53363. eCollection 2020. Biodivers Data J. 2020. PMID: 32874116 Free PMC article.
-
Host Kairomones Influence Searching Behavior of Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), a Parasitoid of Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae).Environ Entomol. 2020 Feb 17;49(1):15-20. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvz155. Environ Entomol. 2020. PMID: 31844882
-
An Effective Cold Storage Method for Stockpiling Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Eggs for Field Surveys and Laboratory Rearing of Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae).J Econ Entomol. 2021 Apr 13;114(2):571-581. doi: 10.1093/jee/toaa307. J Econ Entomol. 2021. PMID: 33459769
-
Impact of the Invasive Brown Marmorated Stink Bug in North America and Europe: History, Biology, Ecology, and Management.Annu Rev Entomol. 2018 Jan 7;63:599-618. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043226. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Annu Rev Entomol. 2018. PMID: 29068708 Review.
Cited by
-
Laboratory and field efficacy of natural products against the invasive pest Halyomorpha halys and side effects on the biocontrol agent Trissolcus japonicus.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 7;15(1):4622. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87325-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39920209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inkley DB. Characteristics of home invasion by the brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Entomol Sci. (2012) 47:125–30. 10.18474/0749-8004-47.2125 - DOI
-
- Horwood M, Milnes JM, Cooper WR. Brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), detections in Western Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Austral. Entomol. (2019) 58:857–65. 10.1111/aen12421 - DOI
-
- Kriticos DJ, Kean JM, Phillips CB, Senay SD, Acosta H, Haye T. The potential global distribution of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys, a critical threat to plant biosecurity. J Pest Sci. (2017) 90:1033–43. 10.1007/s10340-017-0869-5 - DOI
-
- Sparks ME, Bansal R, Benoit JB, Blackburn MB, Chao H, Chen M, et al. . Brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), genome: putative underpinnings of polyphagy, insecticide resistance potential and biology of a top worldwide pest. BMC Genom. (2020) 21:227. 10.1186/s12864-020-6510-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

